Figure 6
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-241115-93
- Publication
- Ono et al., 2024 - Contributions of mirror-image hair cell orientation to mouse otolith organ and zebrafish neuromast function
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
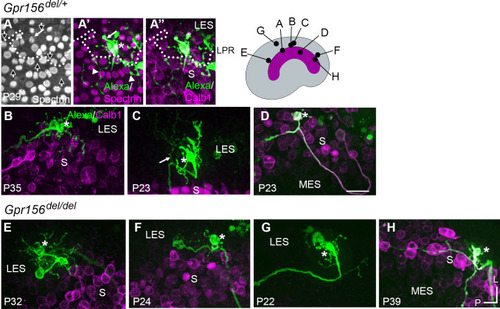
Afferent innervation patterns near the LES/S zone boundary were not substantially disturbed by Gpr156 deletion. Afferent receptive fields (green) were labeled by diffusion of fluorescent dye (AlexaFluor) from whole-cell recording pipettes into calyces (asterisks) and throughout the terminal arbor, for (A–D) Gpr156del/+ controls and (E–H) Gpr156del/del mutants. Counterstained with anti-calbindin (Calb1) antibody to show the striola (magenta). Top right, Schematic of the utricle with magenta striola; black dots, approximate location of each labelled calyx shown. All labeled afferents had a thick, medial-projecting neurite that branched to form up to two calyces and many bouton contacts. Anti-βII-spectrin labeling (A, A’) leaves an unlabeled hole where the kinocilium is, allowing determination of bundle orientation black arrows outlined in white, (A) and, in Gpr156del/+ controls, the LPR (dotted white line). (A) In one control afferent, the receptive field straddled the LPR (A’, A’’), with 1 calyx on a type I HC in the LES (white arrow) and some boutons contacting type II HCs, as terminals or en passant, in the calbindin+ striola (white arrowheads). (B, C). In all other fills, the labeled LES arbors innervated only LES HCs. (C) Arrow, A thin branch extended from the fiber below the epithelium. (D) A receptive field labeled by filling a striolar calyx included 2 calyces and some bouton endings, all restricted to the calbindin+ striola (this afferent is white because of the merge of AlexaFluor and calbindin stains). (E–G) Afferent terminal fields of LES calyces from Gpr156del/del utricles largely remained in the calbindin– region (LES) (E), Figure 6—video 2. (H) A striolar (calbindin+) calyx in a Gpr156del/del mouse made multiple boutons entirely in the calbindin+ area (striola). Scale bar: 20 µm L, lateral; P, posterior. |