- Title
-
Tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase 1 (TDP1) and SPRTN protease repair histone 3 and topoisomerase 1 DNA-protein crosslinks in vivo
- Authors
- Anticevic, I., Otten, C., Vinkovic, L., Jukic, L., Popovic, M.
- Source
- Full text @ Open Biol.
|
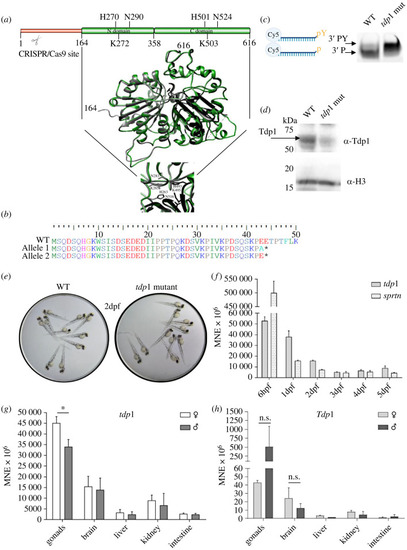
Structural comparison of zebrafish and human TDP1, validation and characterization of the zebrafish |
|
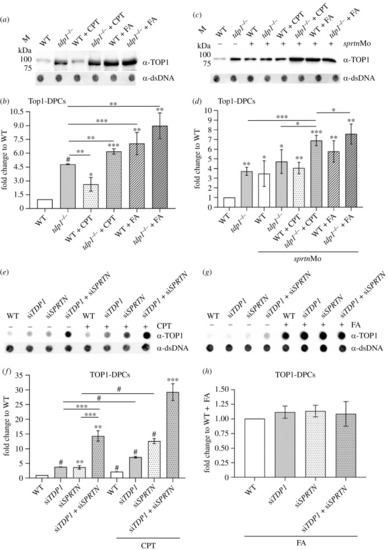
Tdp1 deficiency causes strong accumulation of endogenous and chemically induced Top1-DPCs in embryos and cells. ( |
|
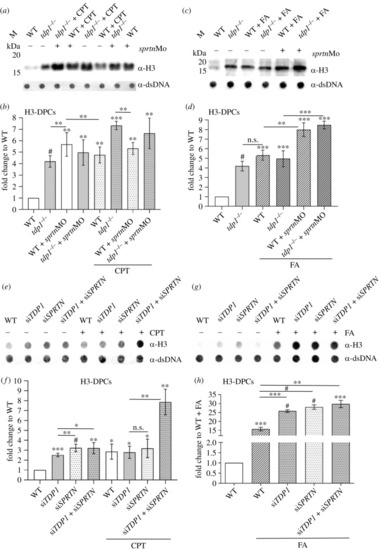
H3-DPC levels are increased |
|
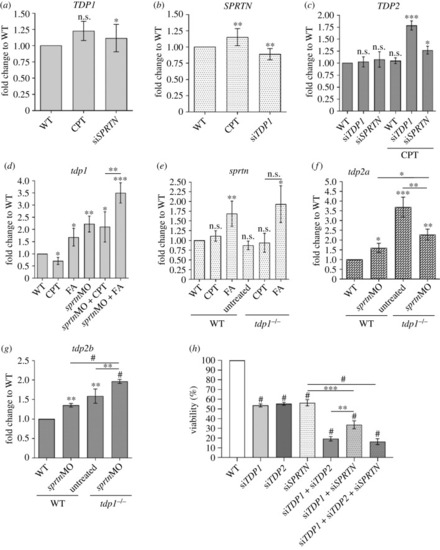
Effects of |
|
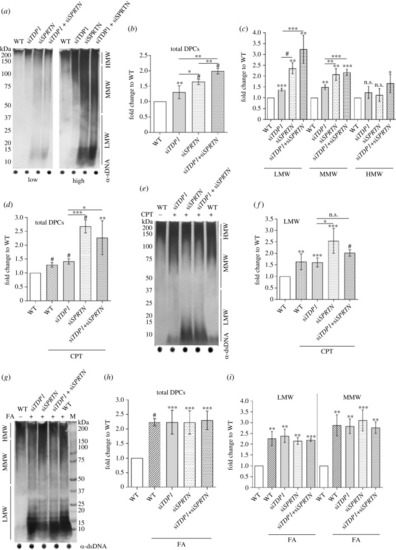
DPC analysis in Tdp1 and Sprtn deficient embryos under physiological conditions and after CPT (10 µM, 1 h) and FA (5 mM, 30 min) treatment. ( |
|
DPC analysis in RPE1 cells after |
|
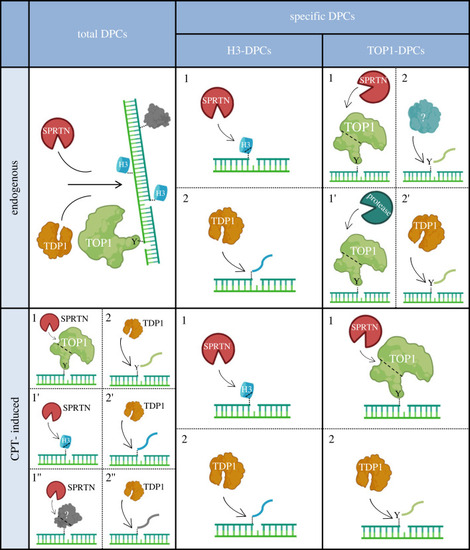
Model of coordinated action of SPRTN and TDP1 in DNA–protein crosslink repair in human cells and zebrafish model. SPRTN is a general DPC protease that cleaves a wide spectrum of crosslinked proteins, whereas TDP1 removes protein residues bound to the 3′ end of the ssDNA break. Under physiological conditions, these two proteins function independently to resolve total DPCs, including specific TOP1-DPCs. Importantly, resolution of endogenous histone-DPCs originating at abasic (AP) sites depends on SPRTN-mediated proteolysis followed by TDP1 phosphodiesterase activity, by which the crosslinked peptide residue is removed from the DNA backbone. In response to the DNA-damaging agent camptothecin, an epistatic relationship between SPRTN and TDP1 is required for the successful removal of histones and TOP1-DPCs as well as other DPCs at the 3′ ends of ssDNA breaks. The model was created with BioRender.com. |