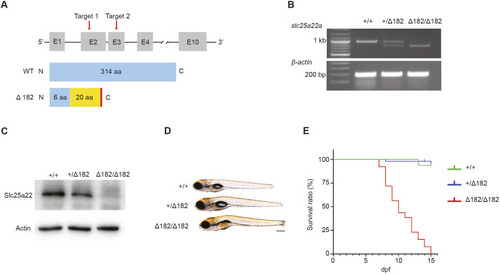
slc25a22aΔ5/Δ5 and slc25a22aΔ182/Δ182 mutants are generated with CRISPR-Cas9 technology. (A) Upper: schematic of the zebrafish slc25a22a locus and location of CRISPR-Cas9 targets (red arrows); lower: schematic of Slc25a22a proteins translated in WT and slc25a22aΔ182/Δ182 mutants generated with the CRISPR-Cas9 technology. The blue and yellow boxes indicate WT and introduced amino acids (aa), respectively, and the red bar represents a premature stop codon. (B) RT-PCR analysis of the targeted slc25a22a region in the indicated alleles. mRNAs were harvested from zebrafish larvae at 5 dpf and amplified with gene-specific primers. β-Actin primers were used for loading control. (C) Western blot analysis of Slc25a22 proteins in 5 dpf larvae with the indicated alleles. Actin protein was used as a loading control. (D) Larvae with the indicated alleles at 5 dpf were imaged under a light microscope. Lateral view anterior to the left. Scale bar: 200 μm. (E) slc25a22a+/+ (n=16), slc25a22a+/− (n=49) and slc25a22a−/− (n=39) embryos were raised to 15 dpf, and their respective Kaplan–Meier survival rate curves were generated.
|