- Title
-
Optimization of genome editing by CRISPR ribonucleoprotein for high efficiency of germline transmission of Sox9 in zebrafish
- Authors
- Yang, K., Cai, L., Zhao, Y., Cheng, H., Zhou, R.
- Source
- Full text @ N. Biotechnol.
|
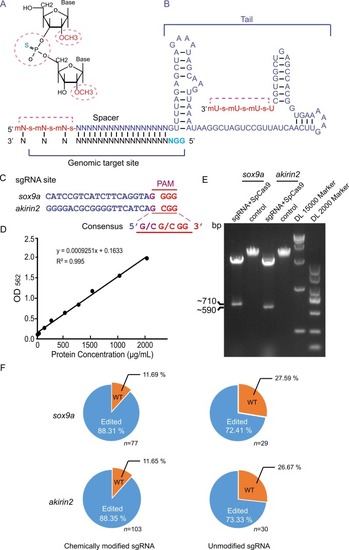
The CRISPR RNP complex with chemically modified sgRNA cuts DNA in vitro and edits the zebrafish genome with high efficiency. A. Schematic diagram of chemical modification sites. The 2′-O-methyl and 3′ phosphorothioate modification sites are indicated in dotted cycles (red). B. The last 3 nucleotides at both ends of the RNA were chemically modified with 2′-O-methyl (m) and 3′ phosphorothioate (s). The last four bases are U at the 3′ end. Chemically modified nucleotides are highlighted in red. The sgRNA was designed with two hairpin structures in the 3′ tail. The target region is located at the 5′ end of the sgRNA. The pan site is denoted by the blue letter. C. Alignment of sgRNA sites highlights consensus sequence of PAM in sox9a and akirin2 genes. D. Quantification of the purified SpCas9 protein concentration determined by a Pierce BCA protein assay kit. E. RNP in vitro cutting efficiency. The target sequences (sox9a or akirin2) were used as the substrates for CRISPR RNP digestion. The cleavage products were examined by 1 % agarose gel electrophoresis. F. Statistical chart of genome editing proportion in zebrafish of the F0 generation. The number of F0 individuals is indicated in the sox9a and akirin2 groups. Unmodified sgRNA groups are controls for modified sgRNAs. WT, wild-type; Edited, gene-edited individuals. |
|
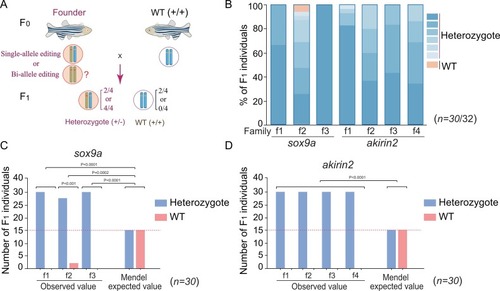
Typing of genome editing and germline transmission. A. Breeding scheme. Founders (F0) are crossed with wild-type animals to determine the transmission of the edited genes in the F1 generation. B. Statistical analysis of the types of edited genes in the F1 generation in 3 families of sox9a (f1 to f3) and 4 families of akirin2 (f1 to f4) after PCR cloning of the edited genes and sequencing. Different shades of blue indicate different types of editing, and the wild-type (WT) is shown in orangesingle bondyellow. n = 30 individuals/family. C, D. Significance testing of the germline transmission ratio of edited genes from the founder to the F1 generation by two-way ANOVA in the sox9a group (C) and the akirin2 group (D). The dotted red lines show the Mendel values. P values are indicated for each group. n = 30 individuals/family. |
|
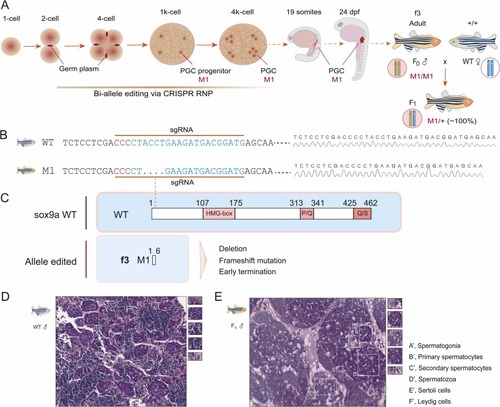
Bi-allele editing, germline transmission, and histology of the edited testis in the sox9a f3 founder. A. Genome editing window during early embryo development, biallelic editing in the first 4 PGC progenitors, and germline transmission. The edited PGCs migrate to their destination to form gonads, in which germ cells have the M1/M1 genotype. M1 indicates the allele 1 edited. The f3 founder crossing with wild-type zebrafish generated all the F1 offspring with the M1/+ genotype. B. DNA sequencing of the edited sox9a gene in the f3 founder and F1 generations. Sequencing diagrams are shown in the right panel. Deletion of 4 bp is indicated in the sgRNA region. The pan sites are denoted in red. C. Schematic diagram of truncated sox9a proteins owing to deletion, frameshift, and early termination compared to the wild type. The HMG box, P/Q, and Q/S domains are denoted in red-shaded boxes. The dotted line indicates the sgRNA site. WT, wild-type. D, E. H&E analysis of the wild-type testis (D) and the sox9a-edited testis in the f3 founder (E). A’, spermatogonia; B’, primary spermatocytes; C’, secondary spermatocytes; D’, spermatozoa; E’, Sertoli cells; F’, Leydig cells. |
|
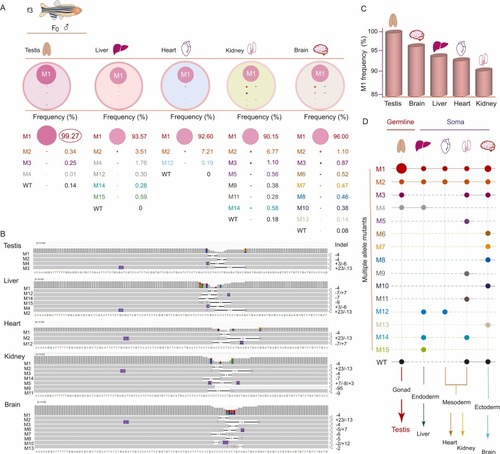
Mapping of edited alleles among the 3 germ layers and future tissue types by deep sequencing. A. Allele typing by indels and frequency in testis and other somatic tissues (liver, heart, kidney, and brain) of the f3 founder. The cycle size in color represents the relative frequency of each allele. M(1,2,…15) indicates edited alleles. WT, wild type. B. Alignments of amplicon sequence variants by an integrative genomics viewer from deep sequencing of genomic DNA in the testis, liver, heart, kidney, and brain. Indels are shown in each edited sequence, and the base number in each indel is indicated on the right. The sequence of wild-type Sox9a is shown at the bottom of each alignment group. C. Percentage of frequency of allele M1 among tissues. D. Mapping of edited alleles and WT alleles among the 3 germ layers and future tissue types (testis and other somatic tissues). Dots in color indicate the alleles edited. WT, wild-type. |
Reprinted from New biotechnology, , Yang, K., Cai, L., Zhao, Y., Cheng, H., Zhou, R., Optimization of genome editing by CRISPR ribonucleoprotein for high efficiency of germline transmission of Sox9 in zebrafish, , Copyright (2025) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ N. Biotechnol.