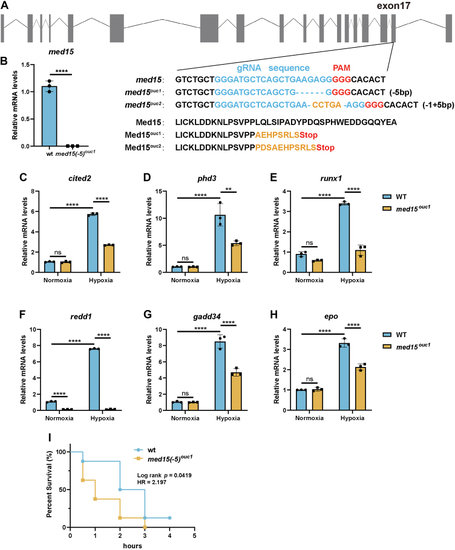
Disruption of med15 in zebrafish suppresses hypoxia signaling.A, information for constructing med15-deficient zebrafish using CRISPR/Cas9 system. B, RT-qPCR analysis of the mRNA levels of med15 in WT or med15-deficient (med15ouc1) zebrafish larvae (3 dpf). Data are represented as means ± SD. n = 3 biologically independent extracts. ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001 by Student's t test. C–H, RT-qPCR analysis of cited2 (C), phd3 (D), runx1 (E), redd1 (F), gadd34 (G), and epo (H) mRNA levels in WT or med15-deficient (med15ouc1) zebrafish larvae (3 dpf) under normoxia (21% O2) or hypoxia (6% O2) for 10 h. Data are represented as means ± SD. n = 3 biologically independent extracts. ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001 by two-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons test. I, Kaplan-Meier survival analysis for WT (n = 8) and med15-null (n = 8) adult zebrafish under 5% hypoxia conditions by log rank test. cited2, CBP/p300-interacting transactivator 2; epo, erythropoietin; gadd34, growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible protein 34; HR, hazard ratio; ns, not significant; med15, Mediator complex subunit 15; phd3, prolyl hydroxylase; redd1, protein regulated in development and DNA damage response 1; runx1, runt-related transcription factor 1.
|