Fig. 5
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-241212-5
- Publication
- Liang et al., 2024 - The intestinal microbiome and Cetobacterium somerae inhibit viral infection through TLR2-type I IFN signaling axis in zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
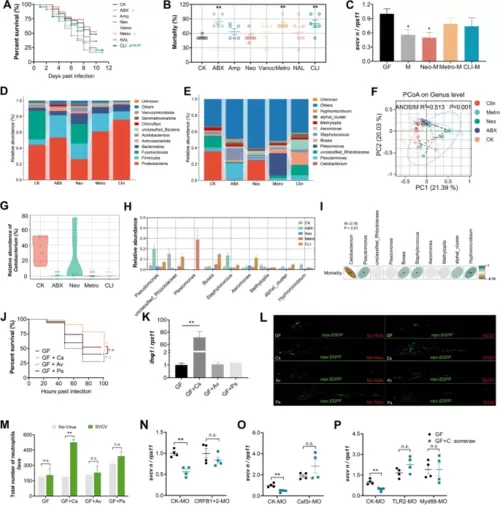
C. somerae recapitulates the antiviral effect of intestinal microbiome. A–B Effect of antibiotics cocktail or single antibiotic feeding on SVCV infection in adult zebrafish. A Survival curve (n = 25). B Mortality (n = 6). C Viral replication in GF zebrafish or GF zebrafish colonized with microbiota derived from adult zebrafish fed with control or antibiotic(s) diet (n = 3, pool of 30 zebrafish larvae per sample). Mock, GF group; M, control microbiota; Neo-M, microbiota from zebrafish fed neomycin; Metro-M, microbiota from zebrafish fed metronidazole; CLI-M, microbiota from zebrafish fed clindamycin. The composition of intestinal microbiota of adult zebrafish fed control or antibiotic(s) diet at phylum (D) and genus level (E) (n = 6, pool of 6 zebrafish per sample). F Principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) of all samples by weighted UniFrac distance at the genus level (n = 6, pool of 6 fish per sample). G The relative abundance of Cetobacterium in intestinal microbiota of adult zebrafish fed control or antibiotic(s) diet (n = 6, pool of 6 zebrafish per sample). H The relative abundance of specific taxa at genus level among groups. I Correlation analysis between the mortality of zebrafish and the relative abundance of genuses (n = 6, pool of 6 fish per sample). J Survival curve of GF zebrafish or GF zebrafish mono-colonized with C. somerae (GF + CS), Aeromonas veronii (GF + AV), or Plesiomonas shigelloides (GF + PS) following SVCV infection (n = 60). K IFNΦ1 expression of GF zebrafish or GF zebrafish mono-colonized with indicated commensal bacterium. Expression was detected at 48 hpi (n = 4, pool of 30 zebrafish larvae per sample). L–M Neutrophils response in mock or SVCV-infected GF Tg (mpx:EGFP) zebrafish or GF counterparts mono-colonized with indicated commensal bacterium. L Confocal imaging of transgenic zebrafish. M Neutrophil numbers (n = 3). Samples were collected for imaging at 48 hpi. Scale bar, 500 μm. Effect of type I IFN receptors knockdown (CRFB1 + CRFB2 MO) (N), depletion of neutrophils (Csf3r MO) (O), and TLR2 and Myd88 knockdown (P) on SVCV infection in GF zebrafish or GF counterparts mono-colonized with C. somerae (n = 4, pool of 30 zebrafish larvae per sample). Viral replication was detected at 48 hpi. A and J log-rank test; B, C, G, H, K one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test; M–P unpaired t-test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, n.s., not significant |