Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-241212-1
- Publication
- Liang et al., 2024 - The intestinal microbiome and Cetobacterium somerae inhibit viral infection through TLR2-type I IFN signaling axis in zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
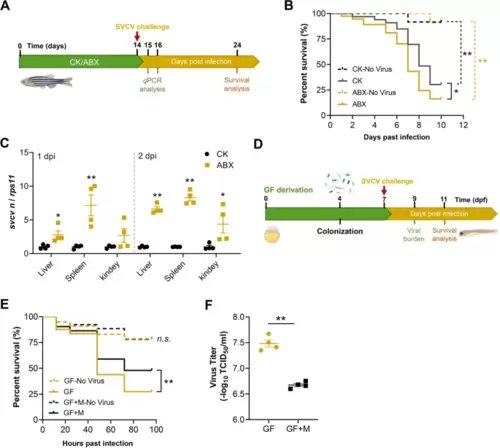
Depletion of intestinal microbiome enhances SVCV infection in zebrafish. A Schematic of the experiment performed in adult zebrafish. B Survival curve of mock or SVCV-infected adult zebrafish fed control or ABX diet (no virus groups: n = 11–12; SVCV groups: n = 39–40). C Viral replication in the liver, spleen, and kidney of SVCV-infected adult zebrafish fed control or ABX diet (n = 4, pool of 6 fish per sample). D Schematic representation for gnotobiotic zebrafish experiment. E Survival curve of mock or SVCV-infected GF and conventionalized zebrafish (n = 80). F Virus titer in GF and conventionalized zebrafish (n = 4, pool of 30 zebrafish larvae per sample). GF, germ-free zebrafish; GF + M, conventionalized zebrafish. B and E log-rank test; C and F unpaired t-test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, n.s., not significant |