Fig. 2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-241212-2
- Publication
- Liang et al., 2024 - The intestinal microbiome and Cetobacterium somerae inhibit viral infection through TLR2-type I IFN signaling axis in zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
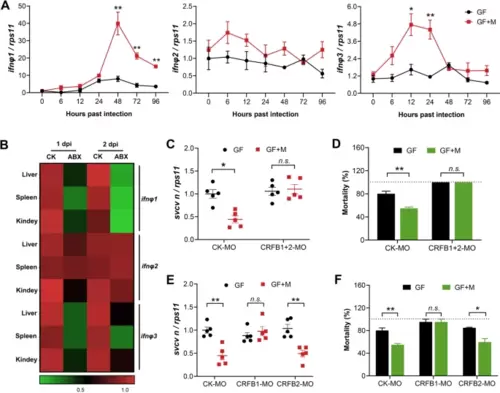
The protective effect of intestinal microbiome against viral infection depends on type I IFN signaling. A Expression of IFNΦ1, IFNΦ2, and IFNΦ3 in SVCV-infected GF or conventionalized zebrafish at different time points (n = 3, pool of 30 zebrafish larvae per sample). B Expression of IFNΦ1, IFNΦ2, and IFNΦ3 in the liver, spleen, and kidney of adult zebrafish after 1 and 2 days post SVCV infection (n = 4, pool of 6 fish per sample). C–D Effect of morpholino-mediated knockdown of type I IFN receptors on SVCV infection. GF and conventionalized zebrafish were treated with control morpholino (CK-MO) or a mixture of CRFB1 and CRFB2 morpholino (CRFB1 + 2 MO) and subjected to SVCV infection. C Viral replication at 48 hpi (n = 5, pool of 30 zebrafish larvae per sample). D Mortality at 96 hpi (n = 3). E–F Effect of morpholino-mediated knockdown of group I or II type I IFN signaling on SVCV infection. GF and conventionalized zebrafish were treated with control morpholino (CK-MO), CRFB1 morpholino (CRFB1-MO), or CRFB2 morpholino (CRFB2-MO) and subjected to SVCV infection. E Viral replication at 48 hpi (n = 5, pool of 30 zebrafish larvae per sample). F Mortality at 96 hpi (n = 3). A, C–F Unpaired t-test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, n.s., not significant |