- Title
-
frizzled5 mutant zebrafish are genetically sensitised to developing microphthalmia and coloboma
- Authors
- Monfries, C., Carter, S., Ataliotis, P., Bseisu, A., Shaikh, M., Hernández-Bejarano, M., Fourteia, M., Maftei, M.I., Young, R.M., Wilson, S.W., Gestri, G., Cavodeassi, F.
- Source
- Full text @ Dis. Model. Mech.
|
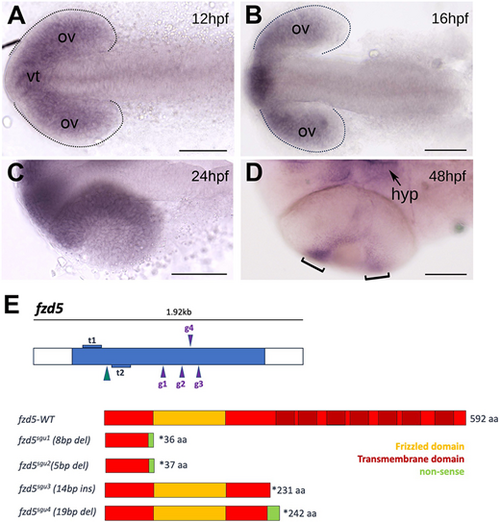
fzd5 is expressed in the optic primordium throughout eye formation. (A-D) Dorsal (A-C) or ventral (D) views, with anterior to the left, at the stage indicated in each panel. Dotted outlines in A and B highlight the optic vesicles. Brackets in D highlight the ciliary marginal zone (CMZ). (E) Schematic of the transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALENs; t1 and t2) and guide RNAs (g1 to g4) used to generate the fzd5 mutant alleles for this study, and their predicted protein products. aa, amino acids; hpf, h post-fertilisation; hyp, hypothalamus; ov, optic vesicles; vt, ventral telencephalon. Scale bars: 100 µm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
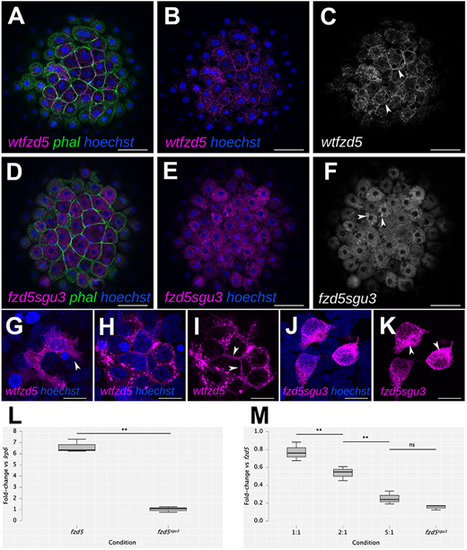
The Fzd5sgu3 protein fails to localise to the cell membrane. (A-K) Cell membrane localisation of wild-type Fzd5-RFP (wt-fzd5-RFP; magenta in A,B,G-I; grey in C; arrowheads in C,G,I) and punctate cytoplasmic accumulation of Fzd5sgu3-RFP (magenta in D,E,J,K; grey in F; arrowheads in F,K) in 4 hpf embryos injected with the corresponding mRNA (A-F), or in HEK293 cells transfected with the corresponding DNA construct (G-K). Embryos were counterstained with phalloidin-488 to reveal cell outlines (green) and Hoechst to reveal cell nuclei (blue). (L) Fold change in luciferase activity of HEK293 cells transfected with lrp6+wt-fzd5-myc and lrp6+fzd5sgu3-myc normalised to activity of lrp6 alone. (M) Fold change in luciferase activity of co-transfections with lrp6+wt-fzd5-myc and increasing levels of fzd5sgu3-myc normalised to activity of lrp6+wt-fzd5-myc alone. Pairwise multiple Student’s t-test comparison between conditions in L and M reveal statistically significant changes in luciferase activity (L, P=0.002; M, P=0.007, P=0.003, P=0.091 from left to right). ns, not significant; **P<0.01. Data pooled from three experiments with four replicates each. Scale bars: 50 µm (A-F) or 10 µm (G-K). |
|
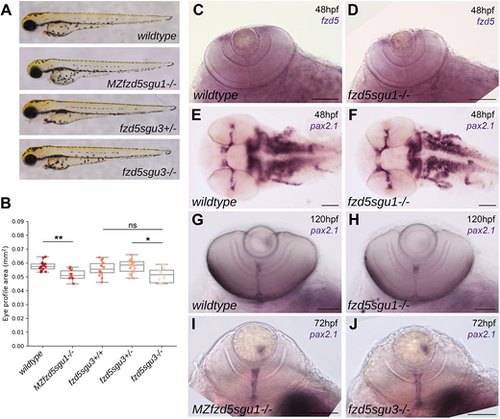
Subtle eye defects in fzd5sgu1, MZfzd5sgu1 and fzd5sgu3 embryos. (A) MZfzd5sgu1 and fzd5sgu3 3 days post-fertilisation (dpf) larvae morphology compared to that of wild-type and heterozygote siblings. (B) Quantifications of projected eye area in the genotypic groups from A. Box plots represent the median and 25-75th percentiles; whiskers indicate the range of the data. Each data point represents one eye. A pairwise Tukey HSD post-hoc test revealed statistically significant eye size differences between the wild-type and the MZfzd5sgu1 group (P=0.006748), and between the fzd5sgu3 homozygote and heterozygote group (P=0.01591). ns, not significant; *P<0.05, **P<0.01. (C-J) Expression of fzd5 in the CMZ (C,D) and pax2.1 in the optic stalk/optic nerve (E-J) in fzd5sgu1 (D,F,H), MZfzd5sgu1 (I) and fzd5sgu3 (J) embryos compared to wild-type controls (C,E,G). Embryo age is indicated in each panel. Scale bars: 100 µm. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
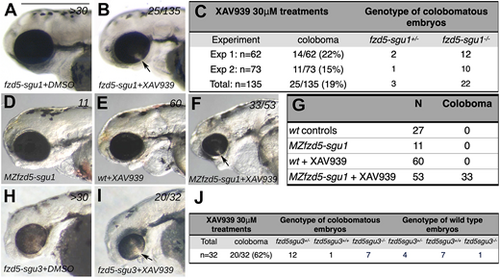
fzd5sgu1 and fzd5sgu3 are genetically sensitised to developing eye malformations. (A,B,D-F,H,I) Lateral views, with anterior to the left, of 72 hpf embryos treated with DMSO (A,D,H) or XAV-939 (B,E,F,I). Colobomas (arrows in B,F,I) are evident in a subset of embryos derived from the incross of fzd5sgu1/+ (B), MZfzd5sgu1 (F) and fzd5sgu3/+ XAV-939-treated embryos (I), a phenotype never observed in wild-type XAV-939-treated embryos (E). (C,G,J) Quantification of phenotypes observed, and their associated genotypes, in XAV-939-treated embryos derived from fzd5sgu1/+ incross (C), wild-type or MZfzd5sgu1 incross (G) and fzd5sgu3/+ incross (J). Scale bar: 500 µm. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
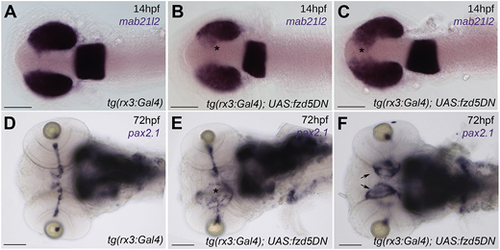
Overexpression of a dominant-negative form of Fzd5 in the optic primordium results in eye defects. (A-C) 14 hpf embryos stained with the pan retinal marker mab21l2 showing incomplete optic vesicle evagination in tg(rx3:Gal4);UAS:fzd5DN [asterisks in B,C, compare with wild-type expression pattern in tg(rx3:Gal4) controls in A]. (D-F) pax2.1 expression at 72 hpf highlighting optic nerve defects and optic disc coloboma in tg(rx3:Gal4);UAS:fzd5DN (E, asterisk; F, arrows) compared to tg(rx3:Gal4) controls (D). Panels show dorsal (A-C) or ventral (G-I) views of embryo heads with anterior to the left. Scale bars: 100 µm. |
|
Abrogation of Fzd4, but not Lrp6, function in fzd5sgu1 heterozygote embryos results in smaller eyes. (A) Experimental pipeline: fzd5sgu1/+ adult carriers were mated, and offspring were injected at one-cell stage with CRISPR guides against the corresponding gene, plus Cas9 mRNA. Embryos were categorised according to eye phenotype, genotyped for fzd5sgu1 mutation and sequenced to confirm the guides' gene editing. HRM, high-resolution melt. (B) Schematic representation of the guides used to interfere with lrp6 (top) and fzd4 (bottom) activity. (C-E) Lateral views, with anterior to the left, of 72 hpf control (C), lrp6 (D) and fzd4 F0 injected fzd5sgu1 embryos. Numbers of embryos in the clutch displaying the phenotype are detailed at the top-right corner of each panel. (F) Quantification of lrp6 and fzd4 F0 injected embryos derived from a fzd5sgu1/+ incross for three and two independent experiments, respectively, detailing the number of embryos showing small eyes and their associated genotypes. (G,H) Projected eye area quantifications of fzd5sgu1 homozygotes and siblings F0 injected with lrp6 (G) and fzd4 (H) CRISPR guides. Box plots represent the median and 25-75th percentiles; whiskers indicate the range of the data. A pairwise Tukey HSD post-hoc test revealed statistically significant eye size differences between the different genotypic groups. ns, not significant; **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. Each data point represents one eye. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
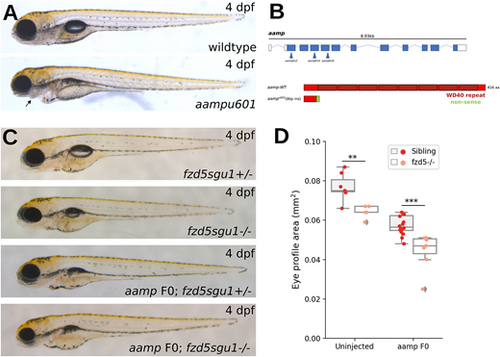
More severe reduction in eye size in fzd5sgu1 homozygotes devoid of aamp function. (A) Phenotype of stable aampu601 mutant (bottom) 4 dpf larvae compared to wild type (top). Arrow indicates missing jaw cartilage. (B) Schematic of predicted protein product from aampu601 allele and representation of CRISPR guides used to target aamp. (C) Representative phenotypes of larvae derived from a fzd5sgu1/+ incross uninjected or injected with aamp guides. Genotype status detailed at the bottom right of each panel. (D) Eye size quantifications of the four genotypic groups shown in C, showing additive effect of fzd5 and aamp loss of function on eye size. Each data point represents one eye. A pairwise Tukey HSD post-hoc test revealed statistically significant eye size differences between the sibling and fzd5sgu1 groups (**P=0.00765794), and between the aampF0 sibling and aampF0;fzd5sgu1 groups (***P=0.00033637). PHENOTYPE:
|