- Title
-
SAMHD1 deficiency enhances macrophage-mediated clearance of Salmonella Typhimurium via NF-κB activation in zebrafish
- Authors
- Martínez-López, A., Tyrkalska, S.D., Martínez-Morcillo, F.J., Abenza-Olmos, C., Lozano-Gil, J.M., Candel, S., Mulero, V., García-Moreno, D.
- Source
- Full text @ Front Immunol
|
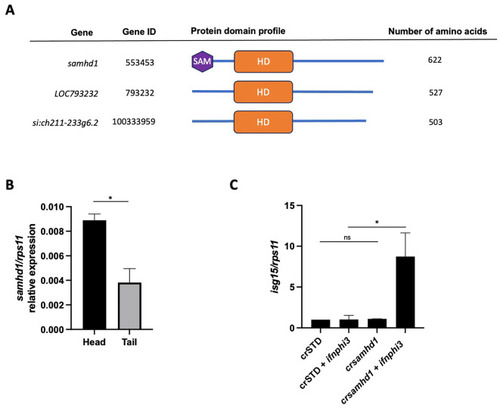
Interferon (IFN) stimulation is required to trigger interferon-stimulated gene (ISG) upregulation in Samhd1-deficient zebrafish larvae. |
|
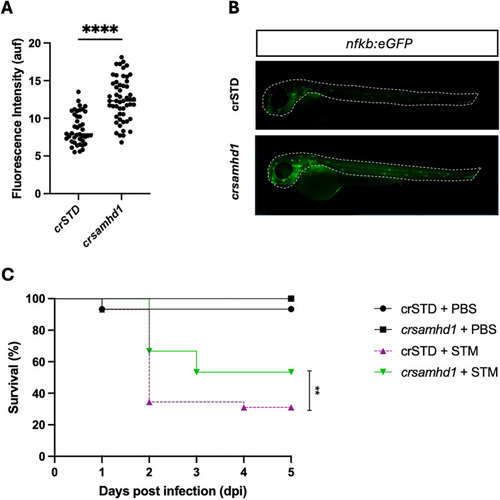
Samhd1 deficiency results in the spontaneous activation of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) and hyperresistance to infection with |
|
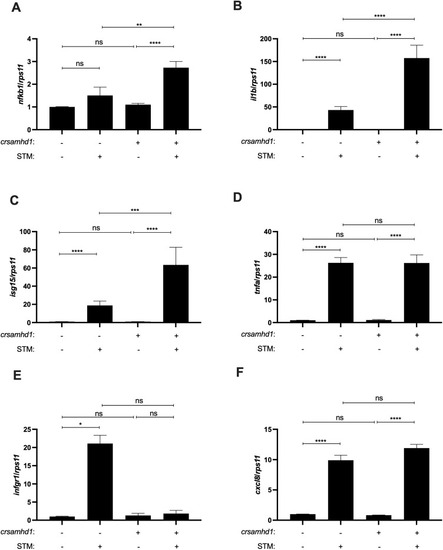
Samhd1 deficiency leads to an activated inflammatory state. |
|
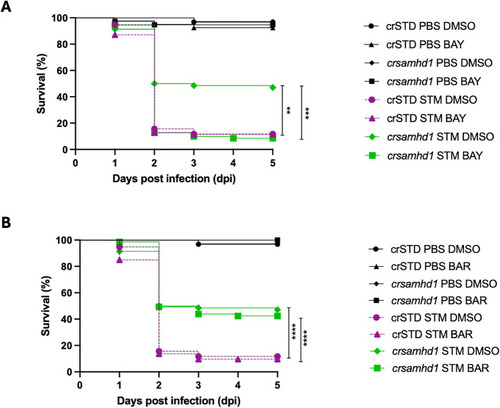
Pharmacological inhibition of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) abolishes the protection of Samhd1-deficient zebrafish larvae to infection with |
|
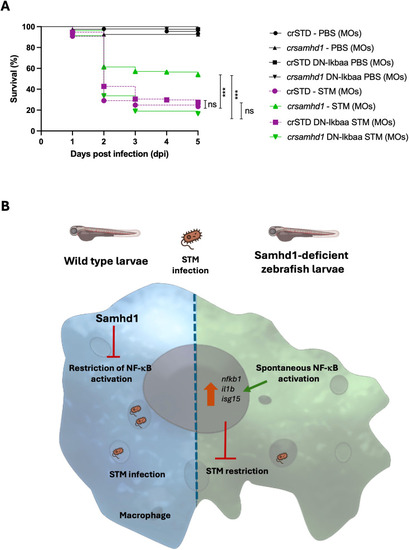
Genetic inhibition of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) in macrophages abolishes the hyperresistance of Samhd1-deficient zebrafish larvae to infection with |