Fig. 4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-250430-9
- Publication
- Wu et al., 2025 - Dynactin knockdown leads to synuclein aggregation by blocking autophagy in a zebrafish model of Parkinson's disease
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
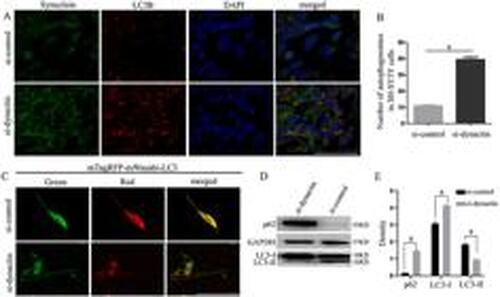
After dynactin knockdown, the autophagosomes formed by synuclein increased abnormally through a blocking pathway. A, Co-labeling of synuclein and LC3B proteins in the si-control and si-dynactin groups was detected in SH-SY5Y cells. Green staining represents synuclein protein, red staining represents LC3B protein, and blue staining represents DAPI-stained nuclei. Scale bar, 100 μm. B, Number of autophagosomes in SH-SY5Y cells. aP<0.0001, compared with the si-control group (t=17.52, df=10). C, Autophagy flow in SH-SY5Y cells in the si-control and si-dynactin groups was detected using the mTagRFP-mWasabi-LC3 plasmid. Scale bar, 50 μm. D, Expression of LC3 and p62 proteins in SH-SY5Y cells was detected by western blot. E, Quantification of p62, LC3-I, and LC3-II relative to GAPDH in panel D. Data are reported as means±SD. aP<0.0001, compared with the si-control group (Student's t-test, n=3 biological replicates). |