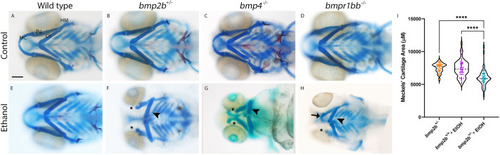
Multiple members of the Bmp pathway display ethanol-sensitive facial phenotypes. (A-H) Whole-mount images showing the viscerocranium of zebrafish larvae at 5 dpf that had been exposed to ethanol (Ethanol) or not (Control). Cartilage is shown in blue, bone in red. Views are ventral, with anterior to the left. Scale bar: 100 μm. MC, Meckel's cartilage; Pq, palatoquadrate cartilage; Ch, ceratohyal cartilage; HM, hyomandibular cartilage. bmp2b+/− or bmp4−/− or bmpr1bb−/− larvae develop comparable to wild-type larvae (A-D). Exposure to 1% ethanol at 10-18 hpf results in a range of defects to the viscerocranium, from loss of MC at the extreme end of this range (asterisks) to reductions in size and changes in shape in the MC (arrow) as well as a flattening of the Ch (arrowheads) (E-H). The average ethanol-induced defects are seen in Bmp mutant alleles but not their wild-type siblings. (I) Violin plot showing area measures of Meckel's cartilage. The size of Meckel's cartilage elements is reduced in ethanol-treated bmp2b+/− larvae compared to ethanol-treated wild-type or untreated bmp2b+/− larvae, with F=36.85, ****P=0.0001, one-way ANOVA, n=29 larvae, both Meckel's cartilage elements per group (n=58 in total).
|

