Fig. 7
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-240912-39
- Publication
- Yang et al., 2024 - Identification of Environmental Compounds That May Trigger Early Female Puberty by Activating Human GnRHR and KISS1R
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
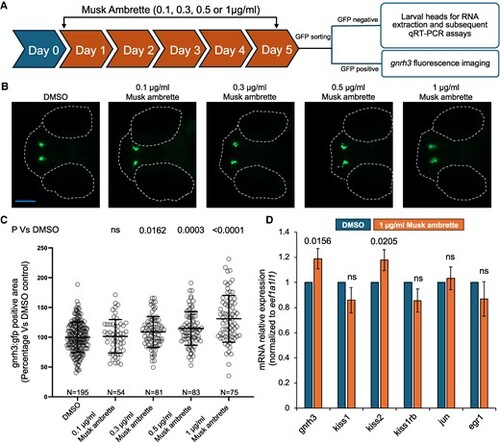
Musk ambrette treatment induces dose-dependent effects on GnRH3 neurons in developing zebrafish. A, Schematic of the experimental workflow. Embryos obtained from adult heterozygous gnrh3:gfp outcrossed with AB wild-type fish were treated with increasing doses of musk ambrette, starting at 1 day post fertilization (dpf) till 5 dpf (n = 15/well/treatment group). At 5 dpf, larvae were sorted for green fluorescent protein (GFP) signal and subjected to live GnRH3 fluorescence imaging or quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) based on the presence or absence of GFP signal, respectively. B, Representative dorsal fluorescent images of gnrh3:gfp larvae at 5 dpf. Anterior, left; posterior, right. Dotted lines indicate eyes and the most anterior region of the head. Scale bar shown in blue, 200 μm. C, Column scatter dot plots show quantification of the GnRH3 GFP-positive area in musk ambrette- or dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO)-treated larvae. At least 2 independent biological replicates for each condition were normalized and pooled to represent percentage vs DMSO control in a single graph. Statistical differences were calculated using an unpaired t test (GraphPad); ns, not significant; error bars represent SD. N = number of larvae. D, Bar graph showing endogenous messenger RNA (mRNA) expression of genes of interest in 5 dpf zebrafish larval heads (human orthologues shown in Supplementary Table S1 (28); kiss2 is a zebrafish paralogue of kiss1 (34). Expression was normalized to eef1a1l1, and statistical differences were calculated using an unpaired t test (GraphPad); ns, not significant; error bars represent SD; n = 25 heads per batch, 3 technical replicates per condition, 3 biological replicates. |