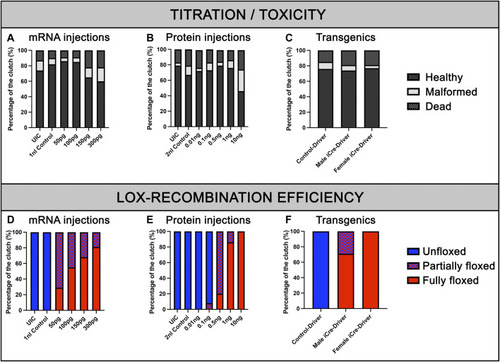
Viability of embryos and recombination efficiencies with iCre-mRNA, Cre-protein or transgenics. (A), Titration of iCre-mRNA injections. Yolk injection of 50 ng/µl, 100 ng/µl, 150 ng/µl, and 300 ng/µl iCre-mRNA, 1 nl Control and uninjected controls (UIC). (B), Titration of Cre protein injections. Cell injection of 0.01, 0.1, 0.5, 1, and 10 ng Cre protein, 2 nl control and uninjected control (UIC). (C), F2 Clutch viability with transgenic iCre expression from F1 iCre-Driver tg(UBI:iCre). (D), Quantification of Lox-recombination following iCre-mRNA injections. Lox-recombination has been assessed based on the detectable conversion/shift of BFP fluorescence to mKate fluorescence. Partial Lox-conversion is evidenced by the combined expression of both BFP and mKate fluorescence, while full Lox-conversion is evidenced by mKate expression with no detectable BFP fluorescence. Results are presented as percentages. (E), Quantification of Lox-recombination following Cre-protein injections. Cre-protein injections ranging from 1 ng to 10 ng were sufficient to trigger robust and reproducible conversions. (F), Quantification of Lox-recombination with transgenics. Female iCre-driver systematically triggered complete and homogeneous Lox-recombination, suggesting a robust effect of iCre mRNA and/or iCre protein maternal deposition.
|

