Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-250521-6
- Publication
- Xu et al., 2025 - Microglia-Derived IL-6 Promotes Müller Glia Reprogramming and Proliferation in Zebrafish Retina Regeneration
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
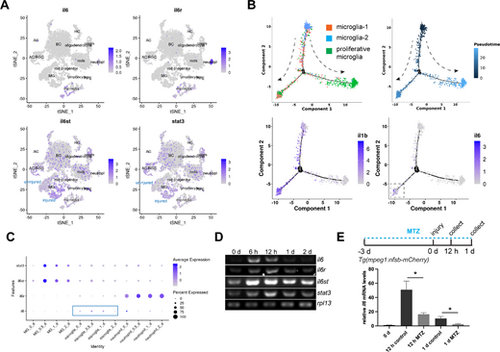
Expression of the IL-6 signaling components in control and stab-injured zebrafish retinas. (A) Single-cell RNAseq analysis showing the expression of il6, il6r, il6st, and stat3 in adult zebrafish retina. (B) Pseudotime analysis showing the expression of il6 and il1b during microglia status transition. The dashed arrows show the direction of the status transition. (C) Dotplot showing the expression of IL-6 signaling component genes in MG, microglia, and neutrophil. (D) PCR analysis showing the expression of il6, il6r, il6st, stat3, and house-keeping gene rpl13 at the indicated time points in zebrafish retina. (E) Microglia ablation using the Tg(mpeg1:nsfB-mCherry) transgenic zebrafish combined with metronidazole (MTZ) treatment abolished injury-dependent retinal il6 expression at 12 hpi and 1 dpi, as shown by qPCR. *, P < 0.05. AC, amacrine cells; BC, bipolar cells; HC, horizontal cells; MG, Müller glia; MTZ, metronidazole; RGC, retinal ganglion cells; RPE, retinal pigment epithelium; tSNE, t-Distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding. |