|
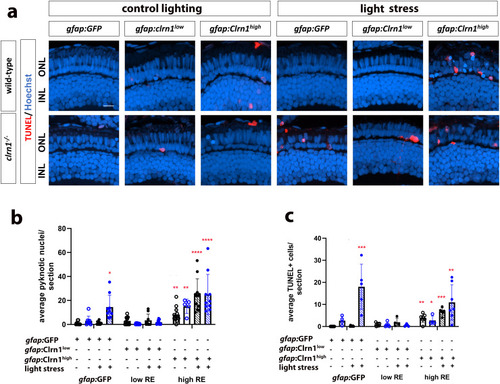
Therapeutic efficacy of Clrn1 re-expression in Müller glia depends on expression level. (a) Retinal images of 7 dpf wild-type (upper rows) and clrn1-/- mutant (lower rows) zebrafish expressing different transgenes (column labels) raised in control lighting conditions (right) or treated from 5-7 dpf with 3500 lux for 48 hours (left, light stress). Hoechst (blue) highlights nuclei of the outer (photoreceptor layer) and inner nuclear layers (labeled ONL and INL) while TUNEL staining (red) highlights dying cells. Quantitation of (b) pyknotic nuclei or (c) TUNEL-positive cells in the ONL reveals that the gfap:Clrn1low transgene decreases sensitivity to light stress induced cell death in clrn1-/- zebrafish while the gfap:Clrn1high transgene induced cell death in clrn1-/- and wild-type zebrafish. (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.005, ****p<0.001; Two-way ANOVA; Significance shown compared to wild-type gfap:GFP without light stress). Error bars=SD. Scale Bar = 50 µm. n=8-12 larvae for each genotype per condition.
|