Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-240426-34
- Publication
- Lee et al., 2024 - Protective effect of alpha-lipoic acid and epalrestat on oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy in zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
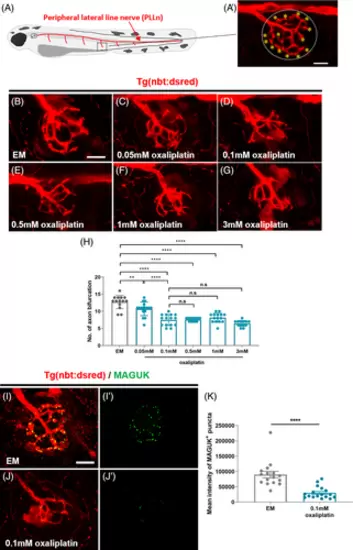
Oxaliplatin causes peripheral neuropathy on PLLn in zebrafish. (A, A′) Schema (A) and fluorescence images (A′) of a sensory nerve in zebrafish PLLn. The dashed circle indicates the neuromast region in the zebrafish peripheral nervous system. The asterisk indicates axon bifurcation of a sensory nerve located in the neuromast. (B–G) Fluorescence images showing sensory nerve terminals located in neuromast in Tg(nbt:dsred) larvae treated with EM (B) and oxaliplatin (C–G) at 9 dpf. (H) Mean number of axon bifurcations from panel (A) to (F). n = 13–15 larvae per group. **p = .0056, ****p < .0001, one-way ANOVA. The data show that oxaliplatin decreases the number of axon bifurcations in PLLn. (I, J′) Fluorescence images showing sensory nerve terminals and postsynaptic MAGUK+ puncta in Tg(nbt:dsred) larvae treated with EM (I, I′) and oxaliplatin (J, J′) at 9 dpf. (K) Mean intensity of MAGUK+ puncta from the panel (I′) and (J′). n = 16 larvae in EM group, n = 17 larvae in 0.1 mM oxaliplatin group. ****p < .0001, t-test. Scale bar, 10 μm in (A), (B), and (I). The data show that oxaliplatin causes the loss of postsynapse in PLLn. ANOVA, analysis of variance. |