Fig. 2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-240426-35
- Publication
- Lee et al., 2024 - Protective effect of alpha-lipoic acid and epalrestat on oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy in zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
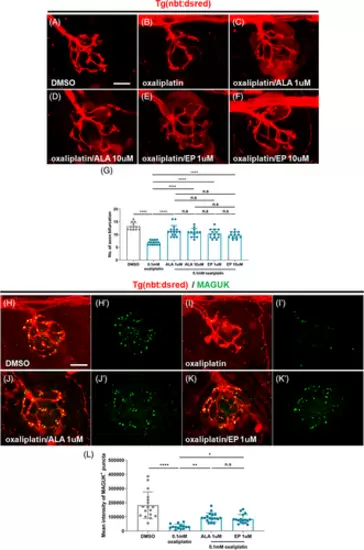
EP protects against OPN in zebrafish. (A–F) Fluorescence images showing sensory nerve terminals located in neuromast in Tg(nbt:dsred) larvae treated with DMSO (A), oxaliplatin (B), and oxaliplatin with ALA (C, D) or EP (E, F) at 9 dpf. (G) Mean number of axon bifurcations from panel (A) to (F). n = 12–16 larvae per group. ****p < .0001, one-way ANOVA. The data show that ALA and EP prevent the defects of sensory axons caused by oxaliplatin in PLLn. (H–K′) Fluorescence images showing sensory nerve terminals and postsynaptic MAGUK+ puncta in Tg(nbt:dsred) larvae treated with DMSO (H, H′), oxaliplatin (I, I′), and oxaliplatin with ALA (J, J′) or EP (K, K′) at 9 dpf. (L) Mean intensity of MAGUK+ puncta from panel (H′, K′). n = 14–17 larvae per group. *p = .0406, **p = .0075, ****p < .0001, one-way ANOVA. Scale bar, 10 μm in (A) and (H). The data show that ALA and EP prevent the loss of postsynapse caused by oxaliplatin in PLLn. ANOVA, analysis of variance. |