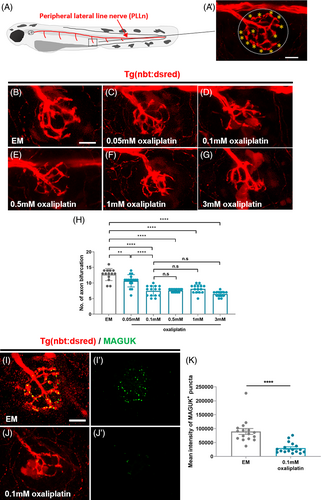
Fig. 1 Oxaliplatin causes peripheral neuropathy on PLLn in zebrafish. (A, A′) Schema (A) and fluorescence images (A′) of a sensory nerve in zebrafish PLLn. The dashed circle indicates the neuromast region in the zebrafish peripheral nervous system. The asterisk indicates axon bifurcation of a sensory nerve located in the neuromast. (B–G) Fluorescence images showing sensory nerve terminals located in neuromast in Tg(nbt:dsred) larvae treated with EM (B) and oxaliplatin (C–G) at 9 dpf. (H) Mean number of axon bifurcations from panel (A) to (F). n = 13–15 larvae per group. **p = .0056, ****p < .0001, one-way ANOVA. The data show that oxaliplatin decreases the number of axon bifurcations in PLLn. (I, J′) Fluorescence images showing sensory nerve terminals and postsynaptic MAGUK+ puncta in Tg(nbt:dsred) larvae treated with EM (I, I′) and oxaliplatin (J, J′) at 9 dpf. (K) Mean intensity of MAGUK+ puncta from the panel (I′) and (J′). n = 16 larvae in EM group, n = 17 larvae in 0.1 mM oxaliplatin group. ****p < .0001, t-test. Scale bar, 10 μm in (A), (B), and (I). The data show that oxaliplatin causes the loss of postsynapse in PLLn. ANOVA, analysis of variance.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Muscle Nerve