Fig. 6
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-231127-99
- Publication
- Zhong et al., 2023 - Eurycomanone stimulates bone mineralization in zebrafish larvae and promotes osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by upregulating AKT/GSK-3β/β-catenin signaling
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
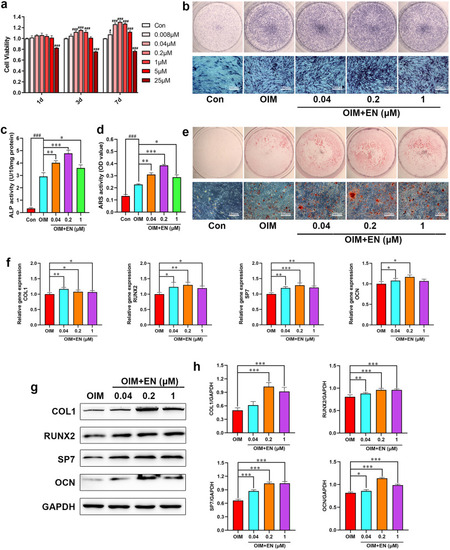
Effects of EN on cell proliferation and osteogenic differentiation in hMSCs. (a) Viability of hMSCs treated with EN at different concentrations (0.008–25 μM). (b–c) ALP staining and activity assays were measured after treating hMSCs with EN (0.04, 0.2, and 1 μM) for 7 days. (d–e) ARS staining and activity assays were performed after 28 days. (f) The mRNA expression levels of osteoblast-related genes (COL1, RUNX2, SP7, and OCN) in hMSCs were detected on day 14. (g–h) The protein expression levels of COL1, RUNX2, SP7, and OCN were detected by western blotting on day 14. #P < 0.05, ###P < 0.001 vs. Con; ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001 vs. OIM. The data are shown as the means ± SD (n = 3). Scale bar: 100 μm. EN, eurycomanone; hMSCs, human mesenchymal stem cells; ALP, alkaline phosphatase; ARS, alizarin red S; COL1, collagen type I; RUNX2, runt-related transcription factor 2; SP7, Sp7 transcription factor; OCN, osteocalcin; Con, Control; OIM, osteogenic induction medium. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.) |