Fig. 9
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-231127-102
- Publication
- Zhong et al., 2023 - Eurycomanone stimulates bone mineralization in zebrafish larvae and promotes osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by upregulating AKT/GSK-3β/β-catenin signaling
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
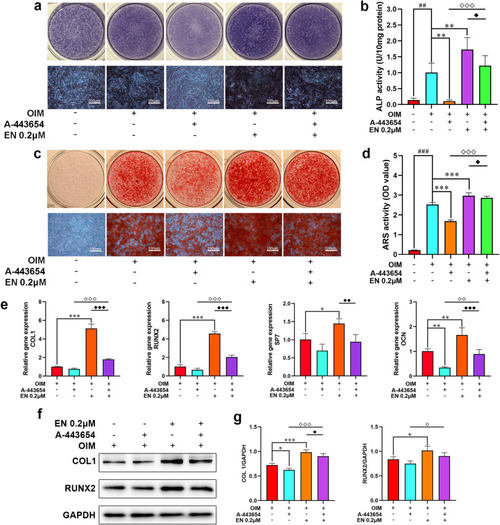
Effects of EN on the intervention with AKT inhibitor A-443654 in hMSCs. (a–b) ALP staining and activity assays were measured after treating hMSCs with EN (0.2 μM) and A-443654 (41 nM) for 7 days. (c–d) ARS was performed on day 28. (e) After exposed to EN and A-443654 for 14 days, the mRNA expression levels of osteoblast-related genes (COL1, RUNX2, SP7, and OCN) in hMSCs were detected. (f-g) The protein expression levels of COL1 and RUNX2 were detected by western blotting on day 14. ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001 vs. Con; ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001 vs. OIM; ◇P < 0.05, ◇◇P < 0.01, ◇◇◇P < 0.001 vs. A-443654; ◆P < 0.05, ◆◆P < 0.01, ◆◆◆P < 0.001 vs. EN. The data are shown as the means ± SD (n = 3). EN, eurycomanone (p-) AKT (phosphorylated-) protein kinase B; hMSCs, human mesenchymal stem cells; ALP, alkaline phosphatase; ARS, alizarin red S; COL1, collagen type I; RUNX2, runt-related transcription factor 2 (p-) GSK-3β (ser9) (phosphorylated-) glycogen synthase kinase 3β at ser9; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; Con, Control; OIM, osteogenic induction medium. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.) |