- Title
-
Identification of KCNE6, a new member of the KCNE family of potassium channel auxiliary subunits
- Authors
- Kasuya, G., Zempo, B., Yamamoto, Y., Ryu, K., Ono, F., Nakajo, K.
- Source
- Full text @ Commun Biol
|
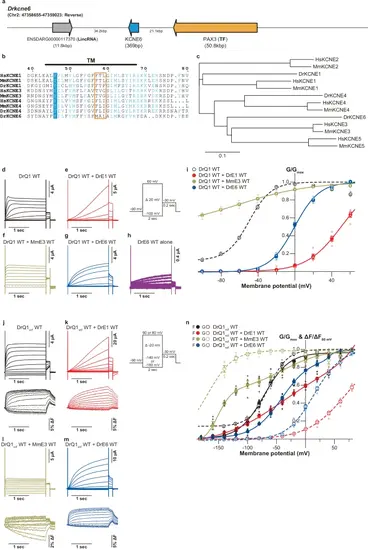
Biophysical properties of zebrafish KCNE1 and KCNE6 proteins.a Genomic region containing the kcne6 ORF sequence in zebrafish. b Sequence alignment around the TM segments of KCNE1, KCNE3, KCNE4, and KCNE6 proteins. c Phylogenetic tree of KCNE1-6 proteins. Sequence alignment was performed and the phylogenic tree was prepared using the EMBL-EBI Job Dispatcher sequence analysis tools framework63. Sequence alignment is shown using ESPript364. Residues corresponding to “the triplet” 51,52 are highlighted with an orange square. For sequence alignment, human KCNE proteins (HsKCNE1, NCBI Accession Number: NP_000210; HsKCNE2, NP_751951.1; HsKCNE3, NP_005463.1; HsKCNE4, NP_542402.4; and HsKCNE5, NP_036414.1), mouse KCNE proteins (MmKCNE1, NP_001349385.1; MmKCNE2, NP_001345301.1; MmKCNE3, NP_001177798, MmKCNE4, NP_067317.1; and MmKCNE5, NP_067462.1), and zebrafish KCNE proteins (DrKCNE1, XP_017213386.1; DrKCNE4, NP_001076366.1; and DrKCNE6) were used. Representative current traces (d–h) and G-V relationships (i) of DrKCNQ1 WT alone and DrKCNE6 WT alone as well as DrKCNQ1 WT co-expressed with DrKCNE1 WT, MmKCNE3 WT, and DrKCNE6 WT. Representative current traces (upper row) and fluorescence traces (lower row) (j–m) and G-V and F-V (n) of DrKCNQ1vcf WT alone as well as DrKCNQ1vcf WT co-expressed with DrKCNE1 WT, MmKCNE3 WT and DrKCNE6 WT. Error bars indicate ± s.e.m. for n = 5 in (i, n). |
|
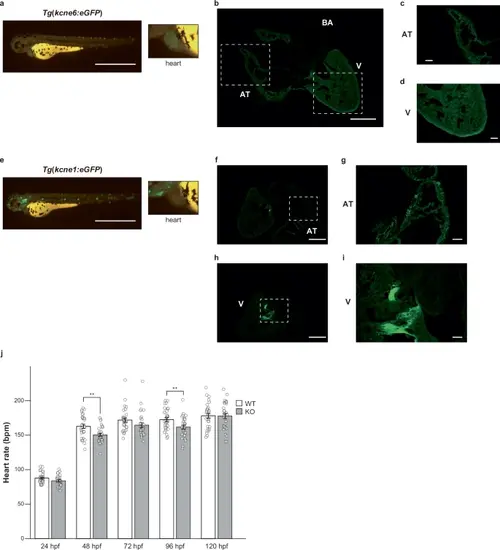
Functional characterizations of KCNE6 in zebrafish.a Representative images of the Tg(kcne6:eGFP) line at 72 hpf under eGFP fluorescence. The scale bar indicates 0.5 mm. The inset shows a close-up view of the heart. b–d Immunofluorescence staining of a heart section from the adult Tg(kcne6:eGFP) line using the anti-GFP antibody. The scale bars indicate 0.5 mm in (b) and 0.1 mm in (c, d). AT atrial myocyte. V ventricular myocyte. BA bulbus arteriosus. e Representative images of the Tg(kcne1:eGFP) line at 72 hpf under eGFP fluorescence. The scale bar indicates 0.5 mm. The inset shows a close-up view of the heart. f–i Immunofluorescence staining of a heart section from the adult Tg(kcne1:eGFP) line using the anti-GFP antibody. The scale bars indicate 0.5 mm in (f, h) and 0.1 mm in (g, i). j Heart rates in the WT and kcne6 KO lines. In each line, ten healthy embryos from three independent pairs (n = 30 in total) were collected at 24 hpf and monitored from 24 hpf to 120 hpf. Student’s t-test was used to compare the WT and kcne6 KO lines and significance was assigned at p < 0.05 (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001). The exact p-values were 0.0013 at 48 hpf and 0.0087 at 96 hpf. |
|
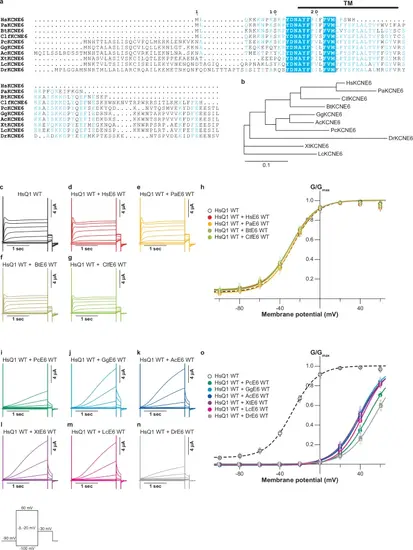
KCNE6 proteins from lower vertebrates are functional.Sequence alignments (a) and phylogenetic tree (b) of KCNE6 proteins from human (HsKCNE6), Sumatran orangutan (Pongo abelii) (PaKCNE6), cow (Bos taurus) (BtKCNE6), dog (Canis lupus familiaris) (ClfKCNE6), koala (Phascolarctos cinereus) (PcKCNE6), chicken (Gallus gallus) (GgKCNE6), green anole (Anolis carolinensis) (AcKCNE6), tropical clawed frog (Xenopus tropicalis) (XtKCNE6), coelacanth (Latimeria chalumnae) (LcKCNE6), and zebrafish (DrKCNE6). Representative current traces (c–g) and G-V relationships (h) of HsKCNQ1 WT alone as well as HsKCNQ1 co-expressed with HsKCNE6 WT, PaKCNE6 WT, BtKCNE6 WT, and ClfKCNE6 WT. Representative current traces (i–n) and G-V relationships (o) of HsKCNQ1 co-expressed with PcKCNE6 WT, GgKCNE6 WT, AcKCNE6 WT, XtKCNE6, LcKCNE6 WT, and DrKCNE6 WT. Error bars indicate ± s.e.m. for n = 5 in (h,o). |
|
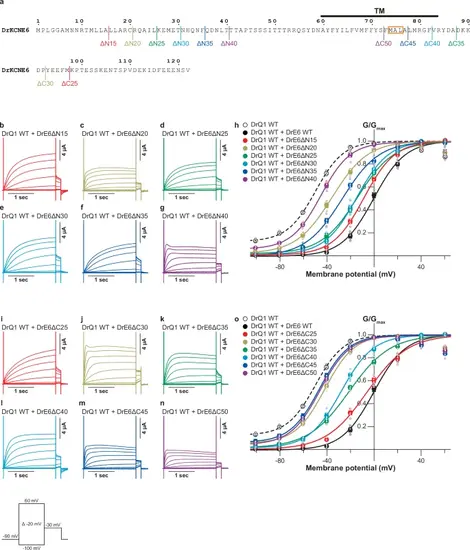
Regions of KCNE6 important for KCNQ1 modulation.a Diagram of N and C termini truncation constructs of DrKCNE6. Representative current traces (b–g) and G-V relationships (h) of DrKCNQ1 WT alone, DrKCNQ1 WT co-expressed with DrKCNE6 WT, and DrKCNQ1 WT co-expressed with each of the N-terminally truncated DrKCNE6 constructs. Representative current traces (i–n) and G-V relationships (o) of DrKCNQ1 WT alone, DrKCNQ1 WT co-expressed with DrKCNE6 WT, and DrKCNQ1 WT co-expressed with each of the C-terminally truncated DrKCNE6 constructs. Error bars indicate ± s.e.m. for n = 5 in (h,o). |
|
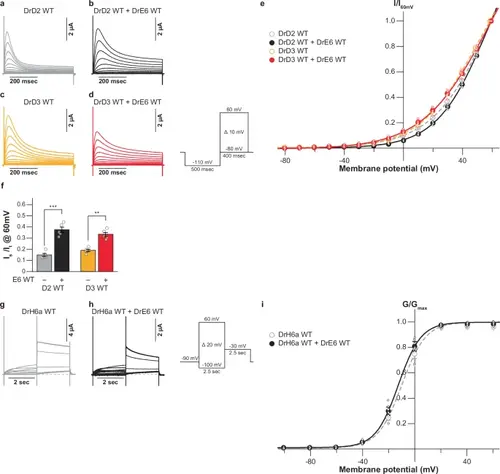
Functional effects of KCNE6 on other Kv channels.Representative current traces (a–d), current-voltage (I-V) relationships (e), and ratios of the sustained to transient currents (f) of DrKCND2 WT and DrKCND3 WT alone as well as them co-expressed with DrKCNE6 WT. Student’s t-test was used to compare KCNDs alone and with DrKCNE6 WT and significance was assigned at p < 0.05 (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001) in (f). The exact p-values were 0.0003 for DrKCND2 and 0.0017 for DrKCND3. Representative current traces (g, h) and G-V relationships (g) of DrKCNH6a WT alone and co-expressed with DrKCNE6 WT. Error bars indicate ± s.e.m. for n = 5 in (e, f, i). |