- Title
-
The food dye Tartrazine disrupts vascular formation both in zebrafish larvae and in human primary endothelial cells
- Authors
- Thanh, D.D., Bich-Ngoc, N., Paques, C., Christian, A., Herkenne, S., Struman, I., Muller, M.
- Source
- Full text @ Sci. Rep.
|
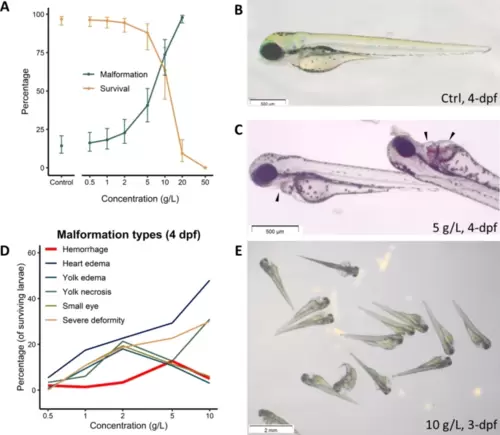
ZET results for TTZ. (A) Dose-response curves showing survival and occurrence of any malformation induced by 96 h TTZ exposure, X-axis is logarithmically scaled. (B) A control embryo at 4 dpf showing normal morphology. (C) Hemorrhagic sites (arrowheads) induced by TTZ exposure. (D) Percentages of surviving embryos with different phenotypes at 4 dpf (Standard Deviations were excluded for visual clarity). (E) Severe deformities at high TTZ concentration. |
|
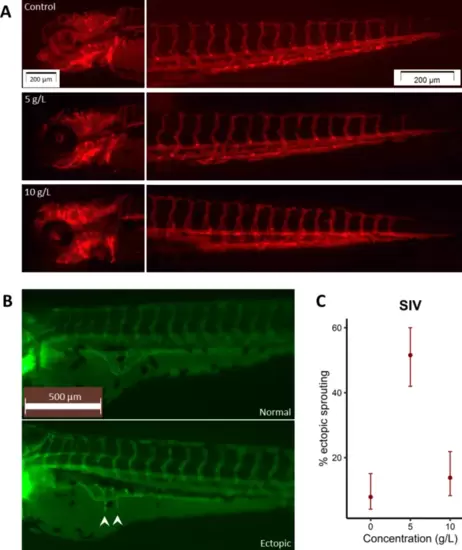
Vascularization analysis on transgenic fluorescent zebrafish lines. (A) Cephalic vessel and caudal venous plexus vascularization are dose-dependently affected by TTZ; Vessels appear to be increasingly merged/clumped together instead of forming distinguishable fine structures; Notably , the three-longitudinal-vessel pattern in the CVP gradually merged (5 g/L) into a two-vessel pattern (10 g/L). (B) Normal (basket-shaped) and ectopically sprouted (arrowheads) SIV formation. (C) Percentages of ectopic sprouting at different TTZ concentrations. |
|
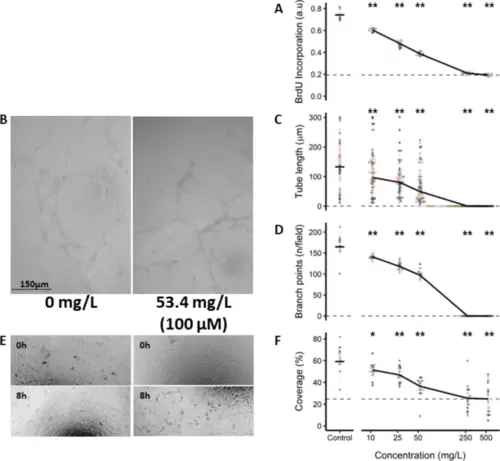
TTZ inhibits HUVEC angiogenic activities in a dose-dependent manner. (A) TTZ inhibits HUVEC proliferation in the BrdU assay. (B-D) TTZ treatment leads to reduced tube extension and branching during tubulogenesis. (E-F) Wound healing assay showing anti-migratory effect of TTZ. Concentrations are log-scaled , and biological replicates are represented using different colors. Asterisks denote statistical significance: *p < 0.01; **p < 0.001. |