Fig. 3
|
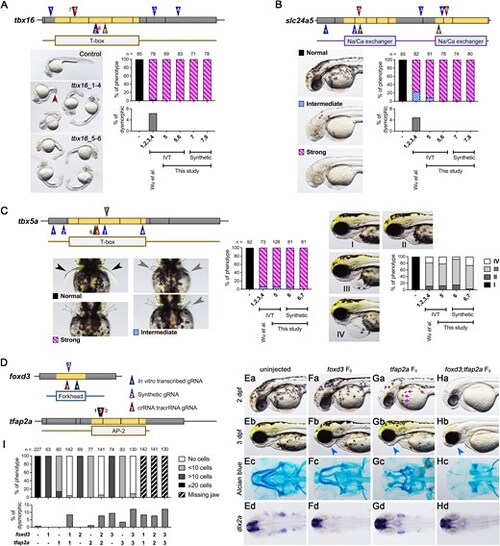
Comparison of phenotype penetrance across current F0 knockout methods. gRNAs targeting tbx16 (A), slc24a5 (B), and tbx5a (C) were obtained either from the methods described by Wu et al. (gRNAs 1–4; blue triangles) or our selection approach (gRNAs 5–8 for tbx16 and slc24a5, and gRNAs 5–7 for tbx5a; brown triangles). These gRNAs were synthesized via IVT or chemical synthesis (green triangles). (A) Tbx16 F0 embryos exhibited a curved tail phenotype at 1 dpf. The brown arrowhead highlights a kinked tail phenotype, which is distinct from the commonly observed curved tail phenotype in tbx16 knockouts. (B) At 2 dpf, slc24a5 F0 embryos displayed a lack of pigment cells, although some F0embryos exhibited dysmorphic phenotypes (Supplementary Fig. S2D). (C) Tbx5a F0 embryos showed both pectoral fin loss and heart edema at 3 dpf. Black arrowheads indicate normal pectoral fins, gray arrowheads indicate shorter or kinked fins, and empty arrowheads denote the absence of pectoral fins. Representative images of heart edema graded I to IV, and corresponding quantifications post-injection are presented in the right panel. (D) Cartoon diagrams illustrate gRNA positions: synthesized via IVT (gRNA_1), chemically synthesized (gRNA_2), or chemically synthesized and assembled into crRNA:tracrRNA complexes (gRNA_3) for foxd3 and tfap2a genes. (E–H) Representative phenotypes for uninjected, foxd3 F0, tfap2a F0, and foxd3;tfap2a F0 embryos include pigmentation phenotypes at 2 dpf (Ea-Ha), aberrant lower jaw morphology at 3 dpf (Eb-Hb), abnormal Alcian blue cartilage staining at 5 dpf (Ec-Hc), and expression patterns of the pharyngeal arch progenitor marker dlx2a (Ed-Hd). Magenta arrows indicate pigment cells, while blue arrows denote aberrant lower jaws. (I) Phenotype quantifications were performed for the number of pigment cells on the yolk sac in 2 dpf embryos and for embryos with missing lower jaws at 3 dpf. Additional dysmorphic phenotypes are shown in Supplementary Fig. S2E. |