Fig. 4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-240229-94
- Publication
- Li et al., 2023 - Bisphenol S remodels red blood cell membrane lipids by altering plasma lipid levels, causing the risk of venous thrombosis in SD rats and zebrafish embryos
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
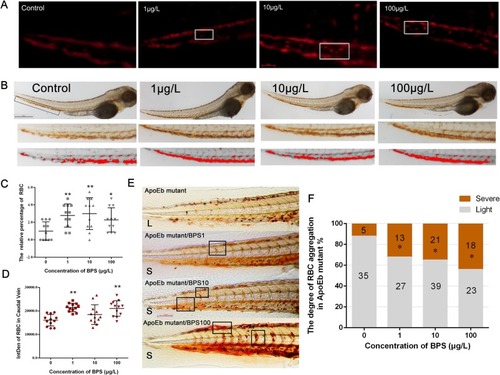
Abnormal adhesion of RBCs in the tail of zebrafish induced by BPS. (A) The screen shots of the videos of RBCs flow in tail blood vessels of zebrafish during 10 s. Scale bar: 50 μm. (B) RBCs were observed by o-diphenylamine staining. Scale bar: 500 μm. (C) The relative percentage of adhered RBCs during 10 s in the caudal vein compared to control group was counted and calculated according to videos. n = 11. (D) The IntDen of RBCs was quantified on the basis of (B). n = 12. (E) O-diphenylamine staining showed the RBC distribution in vessels of ApoEb mutant. Light (L) is defined as few RBC aggregation in the vessels like ApoEb mutant group. Severe (S) is defined as RBCs aggregated in intersegmental vessels/dorsal longitudinal anastomotic vessels/caudal vein like ApoEb mutant/BPS100 group. (F) Percentage of larvae with RBC accumulation degree in vessels was calculated according to (E) (n ≥ 40). The data are expressed as the means ± SDs; * 0.01 < p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01 compared with the control. Videos. RBCs flow in tail blood vessels of zebrafish during 10 s in all treatment groups. |