- Title
-
Development and optimization of an in vivo electrocardiogram recording method and analysis program for adult zebrafish
- Authors
- Duong, T., Rose, R., Blazeski, A., Fine, N., Woods, C.E., Thole, J.F., Sotoodehnia, N., Soliman, E.Z., Tung, L., McCallion, A.S., Arking, D.E.
- Source
- Full text @ Dis. Model. Mech.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
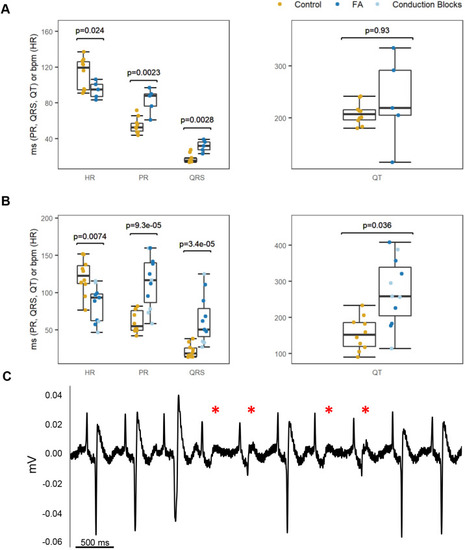
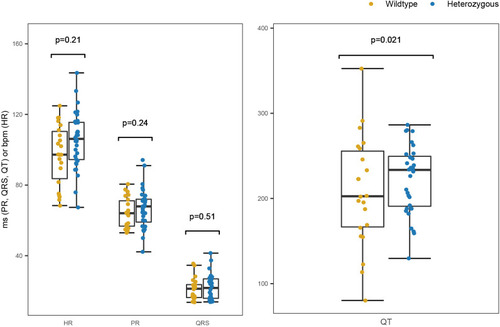
Impact of 0.800 mmol/l FA treatment on adult zebrafish cardiac electrophysiology. (A) Measurements were acquired from 15 adult zebrafish (5.2 months old) dosed for 30 min in either DMSO vehicle control (n=10) or FA (n=5). Compared with controls, FA-dosed fish displayed a slower heart rate (P=0.024) and significant prolongation of PR (P=0.0023) and QRS (P=0.0028) intervals. (B) Measurements were obtained from 21 adult zebrafish (3.5 months old) dosed for 15 min in either DMSO vehicle control (n=10) or FA (n=11). In addition to a significant decrease in heart rate (P=0.0074) and prolongation of PR (P=9.3×10−5) and QRS (P=3.4×10−5) intervals, FA-dosed fish in this experiment also displayed significant QT interval prolongation (P=0.036) compared with control fish. Several FA-dosed fish (n=6) within this independent experiment experienced conduction blocks (light blue points in B). The P-values in A and B were determined from a linear regression adjusting for sex and weight; QT interval was additionally adjusted for heart rate. QT interval plots show the measurement uncorrected for heart rate. (C) Representative trace from a 3.5-month-old male fish dosed with FA for 15 min; the red asterisks denote conduction blocks, as evidenced by the conduction failure (no QRS complex). The trace image was captured using LabChart ‘Zoom View.’ |
|
|