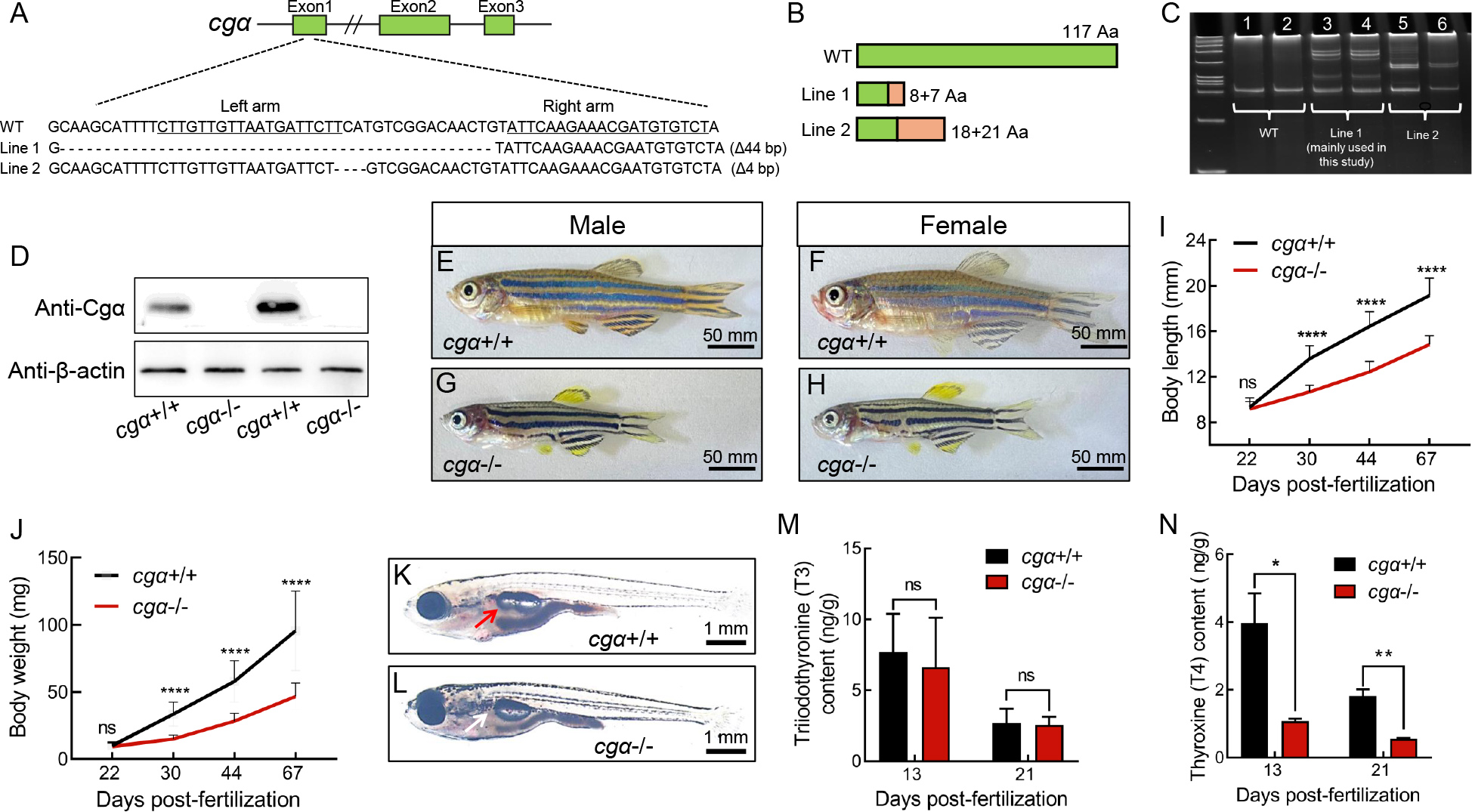
Fig. 1 Generation and characterization of cgα-deficient zebrafish using TALENs A: Schematic of TALEN-mediated editing at exon 1 of the cgα locus. Underlined sequences denote the two targeting arms of TALENs. B: Diagram of WT and two truncated mutant Cgα proteins in zebrafish. Green regions represent amino acid sequences identical to WT, while orange regions indicate mismatched residues. C: Heteroduplex-based genotyping of cgα in cgα+/+ control fish (Lanes 1 and 2) and cgα+/− fish (Lanes 3 and 4 for mutant line 1; Lanes 5 and 6 for mutant line 2), amplified products from tail gDNA samples. D: Western blot analysis of Cgα in pituitary samples from control and mutant lines of cgα-deficient male zebrafish. E–H: Gross appearance of control siblings (E, control male; F, control female) and cgα-deficient fish (G, mutant male; H, mutant female) at 4 mpf. I, J: Body length (I) and weight (J) of control siblings and cgα-deficient fish from juvenile to adult stages. K, L: Gross appearance of control sibling (K) and cgα-deficient fish (L) at 16 dpf. Red arrow indicates inflated anterior swim bladder of control fish, white arrow indicates undeveloped anterior swim bladder of cgα-deficient fish. M, N: Levels of triiodothyronine (T3, M) and thyroxine (T4, N) in bodies of control and cgα-deficient fish at 13 and 21 dpf stages. ns: Not significant; *: P<0.05; **: P<0.01; ****: P<0.0001.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Zool Res