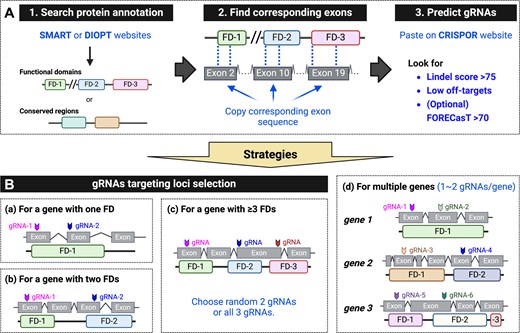
Fig. 6 Standardized gRNAs selection and strategies for F0 mutagenesis. (A) Steps for finding a gRNA: (1) Identify functional domains (FDs) or conserved regions using resources like the SMART website (http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/) or the DIOPT database (https://www.flyrnai.org/diopt). (2) Obtain the nucleotide sequence encoding the functional domain. (3) Enter the nucleotide sequence into the CRISPOR website (http://crispor.tefor.net/), select the desired genome and protospacer adjacent motif (PAM), and submit. Prioritize gRNAs with a Lindel score > 75 (outcome score), and as few off-target matches as possible. If no predicted values are shown, extend the input sequence by ∼200 base pairs. (B) Strategies for designing gRNAs to target loci in various scenarios: (a) For a gene encoding one FD, select two gRNAs: one targeting the beginning of the FD and another targeting the middle. (b) For a gene encoding two FDs, select two gRNAs, each targeting a different domain. (c) For a gene encoding more than three FDs, select two gRNAs targeting any two FDs, or three gRNAs targeting any three FDs. (d) For targeting multiple genes, select one to two gRNAs per gene, targeting FDs. Up to six gRNAs can be co-injected without observed toxicity.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Nucleic Acids Res.