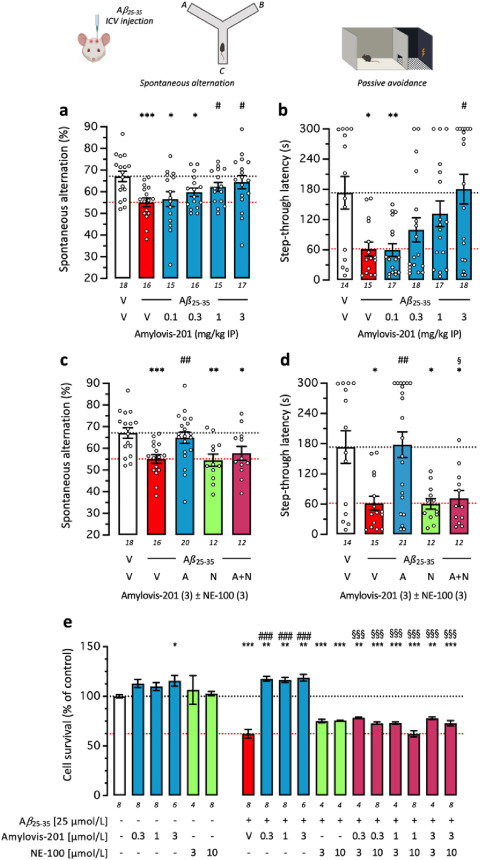
Fig. 4 Amylovis-201 attenuated Aβ25–35-induced learning impairment in mice and Aβ25–35-induced cytotoxicity in SH-SY5Y cells through σ1 agonism: dose–response effects in the (a) spontaneous alternation in the Y-maze and (b) step-through passive avoidance. (c, d) Blockade of Amylovis-201 effect by NE-100 in each test. Mice received oligomerized Aβ25–35 peptide (9 nmol, icv) or vehicle solution and then Amylovis-201 (0.3–3 mg/kg ip) 7 days before behavioral analyses. The Y-maze session was performed on Day 7 (a, c) and passive avoidance training on Day 8 and retention on Day 9 (b, d). In (c, d), NE-100 was administered at 3 mg/kg ip simultaneously with Amylovis-201 at 3 mg/kg IP. (e) SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells (10,000 cells/well) were exposed to Aβ25–35 (25 μmol/L) and Amylovis-201 (0.3–3 μmol/L) and/or NE-100 (3, 10 μmol/L). Cell survival was monitored after 24 h using the MTT assay. Abbreviations: V, vehicle solution (physiological saline); A, Amylovis-201; N, NE-100. Data show mean ± SEM of the number of determination indicated within or below the columns. ANOVAs: F(5,90) = 3.336, P = 0.0082 in (a); F(4,72) = 5.109, P = 0.0011 in (c); F(11,80) = 49.51, P < 0.0001 in (e). Kruskal–Wallis ANOVAs: H = 13.5, P = 0.0019 in (b); H = 14.18, P = 0.007 in (d). ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001 vs. (V + V)-treated mice or untreated cells; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001 vs. (Aβ25–35+V)-treated mice or cells; §P < 0.05, §§§P < 0.001 vs. (Aβ25–35 +Amylovis-201)-treated mice or cells; Dunnett's test in (a, c, e), Dunn's test in (b, d).
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Acta Pharm Sin B