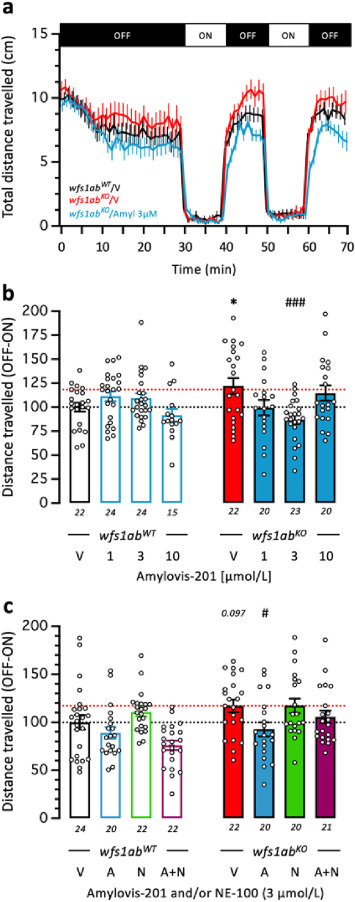
Fig. 2 Amylovis-201 attenuated the hyperlocomotor response of 5 dpfwfs1abKO mutant zebrafish larvae in the VMR test through σ1 agonism: (a) VMR activity profiles of V-treated wfs1abWTand wfs1abKO mutant lines and wfs1abKO zebrafish treated with Amylovis-201 at 3 μmol/L; (b) dose–response effect of Amylovis-201 on the zebrafish mobility; and (c) effect of NE-100. The fish mobility was measured for 70 min, with 30 min of training in the dark (OFF), then 2 cycles of light/dark (ON/OFF) of 10 min each. In (b, c), the distance traveled by wfs1abWT and wfs1abKO larvae during the light/dark cycle was averaged as differences between the OFF and ON phases. Data show mean ± SEM of the number of animals indicated below the columns. Two-way ANOVAs: F(1,162) = 0.4218, P = 0.5170 for the genotype, F(3,162) = 1.316, P = 0.2710 for the treatment, F(3,162) = 5.561, P = 0.0012 for the interaction in (b); F(1,163) = 9.608, P = 0.0023 for the genotype, F(3,63) = 6.781, P = 0.0002 for the treatment, F(3,163) = 1.616, P = 0.1876 for the interaction in (c). ∗P < 0.05 vs. V-treated wfs1abWT zebrafish; #P < 0.05, ###P < 0.001 vs. V-treated wfs1abKO zebrafish; Dunnet's test.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Acta Pharm Sin B