|
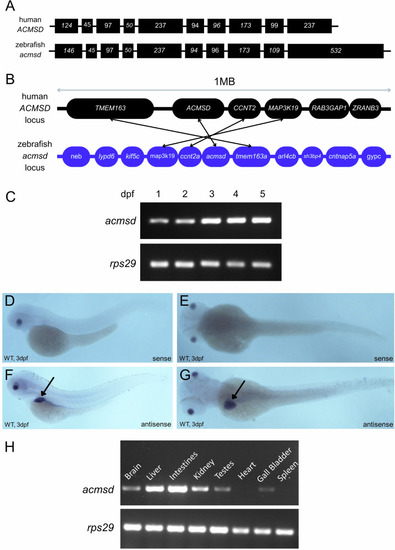
acmsd is expressed primarily in the liver and intestines of wildtype zebrafish. A Exonic structure of ACMSD. Human ACMSD (ENSG00000153086) has a single orthologue in zebrafish (ENSDARG00000062549) which shares 81% sequence homology with its human counterpart (based on CLUSTAL W v1.81 data). B Synteny has been retained between species. The region comparison feature on Ensembl was used to compare a 1 Mb region around the Acmsd gene on human chromosome 2 and zebrafish chromosome 9. Not all genes in the region are included. Orthologous genes are identified by arrows. C RT-PCR demonstrated acmsd expression with an increasing concentration from 1 to 5dpf in acmsd+/+ larvae. In situ hybridisation demonstrated restricted acmsd expression to the liver (arrows) and gut at 3dpf, shown from lateral (F) and dorsal (G) views. The sense probe produced no staining (D, E). H RT-PCR demonstrated acmsd expression primarily in the liver and intestines of both adult male (shown) and adult female (not shown) zebrafish. Expression was also identified in the brain, kidney, gonad,s and gall bladder.
|