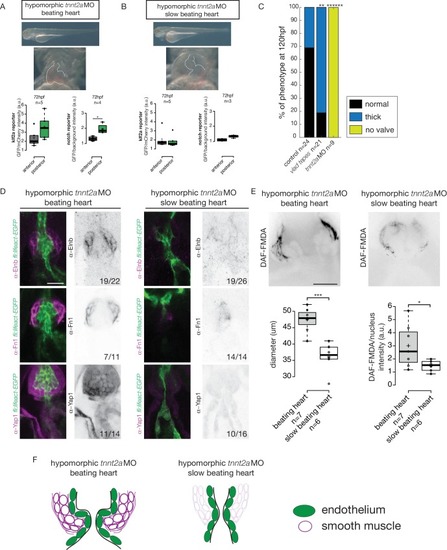
Klf2a and notch response, as well as the smooth muscle cell identity, are flow-dependent. Quantification of the Klf2a and Notch reporter expressions in tnnt2a-morpholino injected embryos showing a ‘beating heart’ (p=0,27 and p=0,01 respectively). (A) and a ‘slow beating heart’ (p=0,7 and p=0,1 respectively) (B) at 72 hpf. N = 2 independent experiments. (C) Quantification of the phenotypes in the control (n = 24), vlad tepes mutant (n = 21 embryos from two independent experiments), tnnt2aMO-injected embryos (n = 9 embryos from two independent experiments). Chi-square test. **: p<10−2, ******: p<10−6. (D) Z-sections of the Tg(fli:lifeact-eGFP) counterstained with either Fibronectin1 (Fn1), elastin (Elnb) or Yap1 in tnnt2a-morpholino injected embryos (slow beating and beating heart). Scale bar: 20 µm. N = 2 independent experiments. (E) Z-section and quantification of the BA diameter and DAF-FMDA intensity in tnnt2a-morpholino injected embryos (p=0,0005 and p=0,05 respectively). Student’s t-test. Boxplots: Center lines show the medians; box limits indicate the 25th and 75th percentiles as determined by R software; whiskers extend 1.5 times the interquartile range from the 25th and 75th percentiles, outliers are represented by dots. (F) Scheme summarizing the down-regulation of the smooth muscle markers in ‘slow beating heart’ embryos compared to ‘beating heart' embryos.
|

