FIGURE
Fig. S1
Fig. S1
|
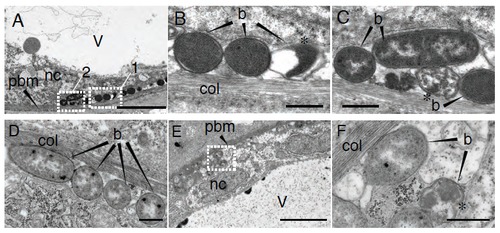
E. coli remains extracellular in the notochord of infected larvae. Ultra-structural analysis using transmission electron microscopy of notochord infected larvae with E. coli, 15 min after infection (A-C) and 2 hpi (D-F). (B) and (C) are high magnification of regions boxed in (A), box 1 and 2, respectively. and (F) of region boxed in (E). Asterisks show bacteria whose morphology is altered. b: bacteria, pbm: peri-notochordal basement membrane, col: collagen sheath, nc: notochordal cell, v: vacuole. Scale bars : 5 μm in A and E, 0.5 μm in B, C, D and F. |
Expression Data
Expression Detail
Antibody Labeling
Phenotype Data
Phenotype Detail
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Dis. Model. Mech.