|
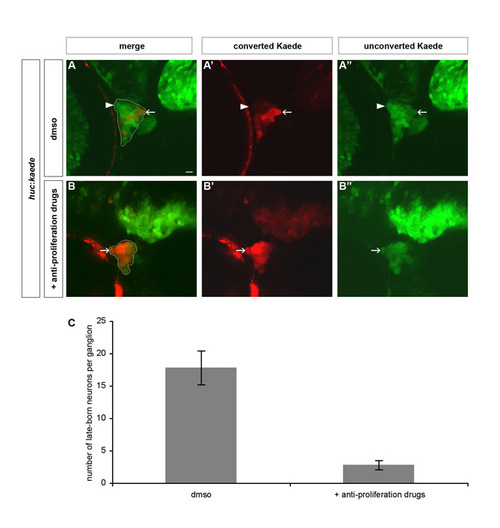
Blocking proliferation eliminates late-born neurons in trigeminal sensory ganglia. To remove late-born neurons from the trigeminal sensory ganglia, proliferation was blocked after 24 hpf by treating embryos with anti-proliferative drugs. (A,B) Wild-type embryos were treated with 2% DMSO alone (A) or 20 mM hydroxyurea and 150 μM aphidicolin (B). Embryos were analyzed using BAPTI at 72 hpf. Late-born neurons contain only green, unconverted, Kaede (white arrowhead), whereas early-born neurons also contain red, converted, Kaede (white arrow). (C) The chart represents the number of late-born neurons per trigeminal sensory ganglion in treated and mock-treated embryos. Late-born neurons are severely reduced or absent upon treatment with the anti-proliferative drugs. The error bar refers to the standard error.
|