- Title
-
The Interaction Between the asb5a and asb5b Subtypes Jointly Regulates the L-R Asymmetrical Development of the Heart in Zebrafish
- Authors
- Zhou, W., Cai, W., Li, Y., Gao, L., Liu, X., Liu, S., Lei, J., Zhang, J., Wang, Y., Jiang, Z., Wu, X., Fan, X., Li, F., Zheng, L., Yuan, W.
- Source
- Full text @ Int. J. Mol. Sci.
|
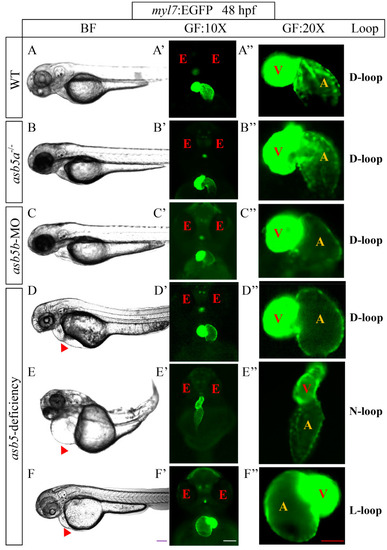
The impact of |
|
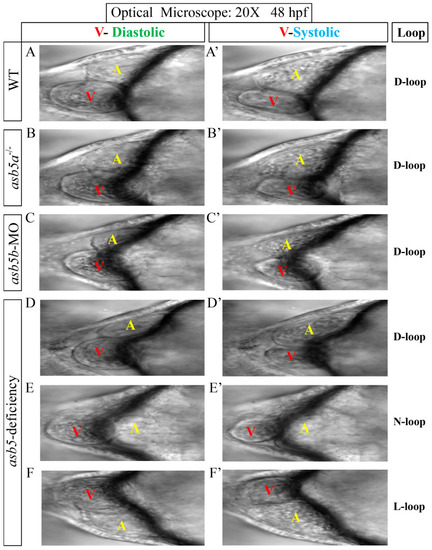
The morphological changes following the inactivation of |
|
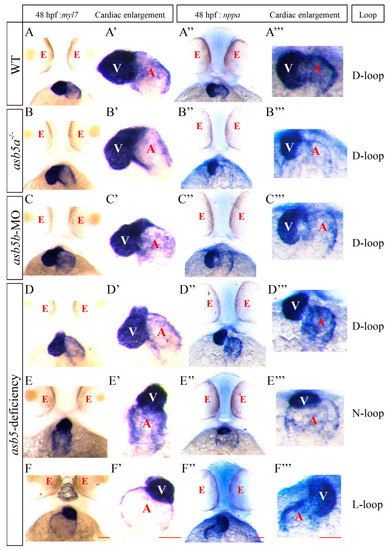
WISH analysis of heart looping at 48 hpf in the |
|
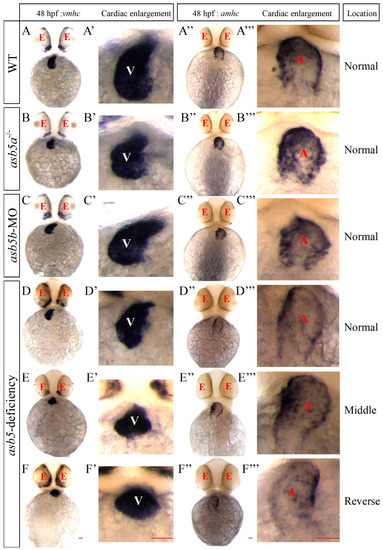
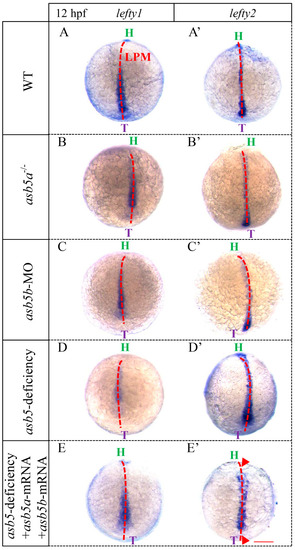
WISH results using |
|
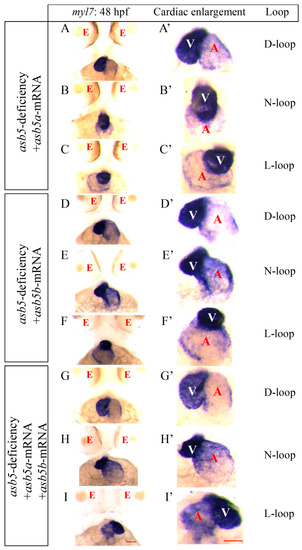
Rescue experiments conducted on the |
|
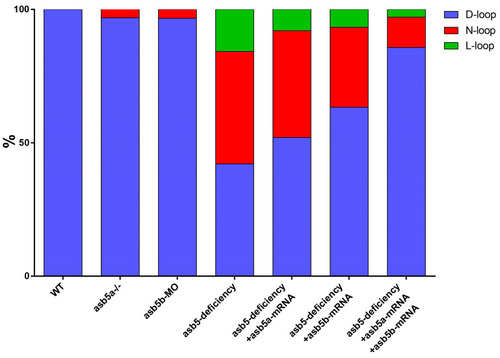
Statistical chart of rescue experiments conducted across various groups. WT: Wild-type control group. |
|
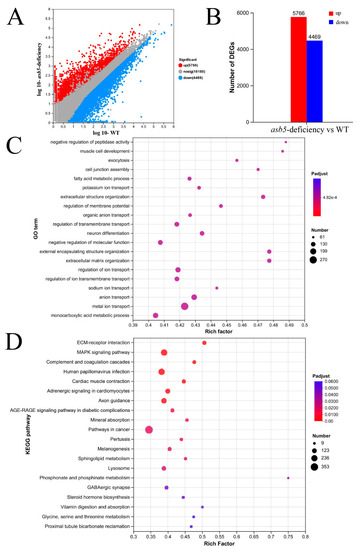
The impact of |
|
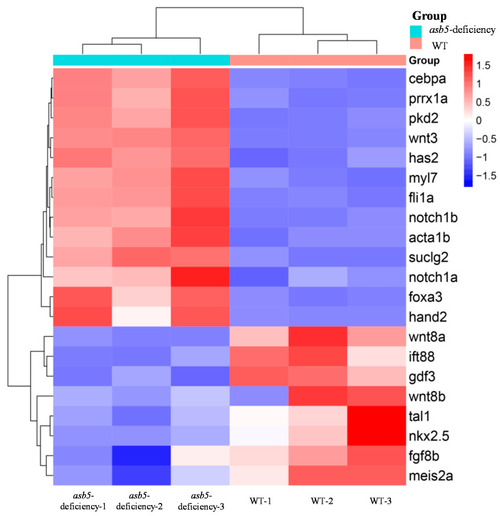
Summary chart of RNA-Seq data for the regulation of asymmetrically developing genes in 48 hpf |
|
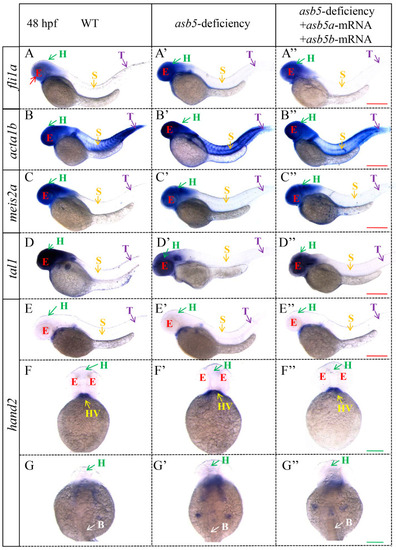
WISH results for genes associated with L-R asymmetric development in 48 hpf |
|
WISH results for other genes related to L-R asymmetric development in |
|
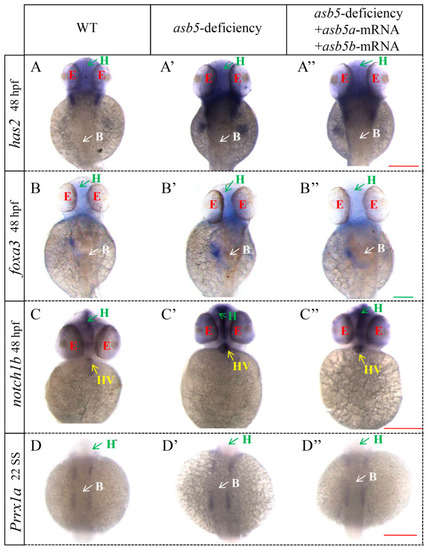
WISH results utilizing |
|
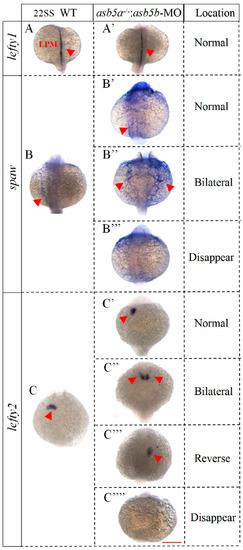
WISH results in WT and the |
|
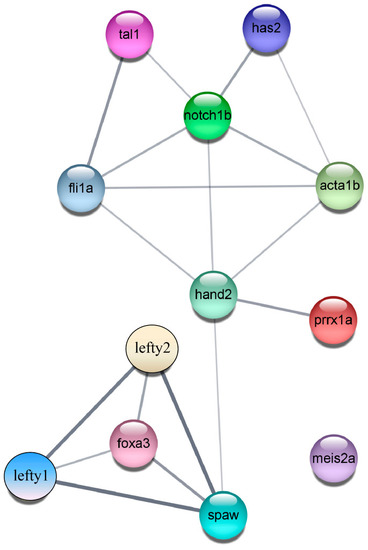
PPI regulatory network diagram. The PPI network comprises three modules, consisting of a total of 12 nodes and 18 edges. |
|
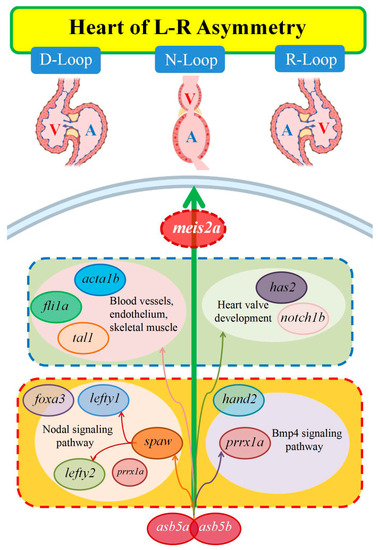
This molecular regulatory network diagram illustrates the influence of |