- Title
-
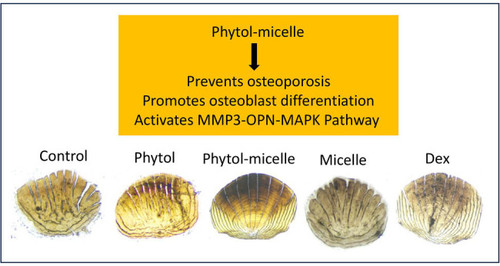
Phytol-mixed micelles alleviate dexamethasone-induced osteoporosis in zebrafish: Activation of the MMP3-OPN-MAPK pathway-mediating bone remodeling
- Authors
- Liu, B., Wang, P., Lv, X.
- Source
- Full text @ Open Life Sci
|
|
|
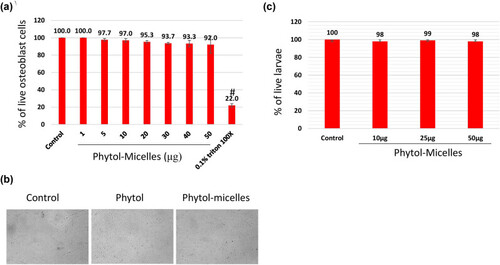
Biocompatibility assessment of phytol-micelles. MG63 cells treated with varying phytol-micelles concentrations (0–50 μg) for 48 h showed no toxicity (a) representative cell image following exposure to 50 μg of phytol-micelles for 48 h. The image shows the cellular morphology and there are no any notable changes induced by the treatment (b). Zebrafish larvae treated with phytol-micelles (50 μg) showed no toxicity (c). # indicates a significant decrease. |
|
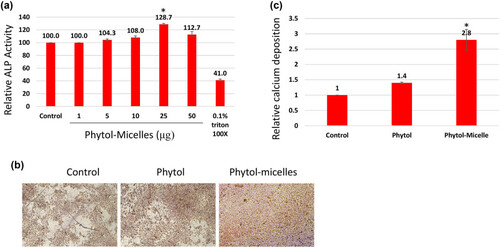
Effects of phytol-micelles on osteoblast differentiation and mineralization. MG63 cells treated with varying phytol-micelles concentrations (5–50 μM) for 7 days showed increased ALP activity, notably higher at 25 μg (a). Treatment with 25 μg phytol-micelles for 14 days enhanced calcium deposition, indicating the potential for osteoblast differentiation and mineralization (b) and quantification (c). * indicates a significant increase. |
|
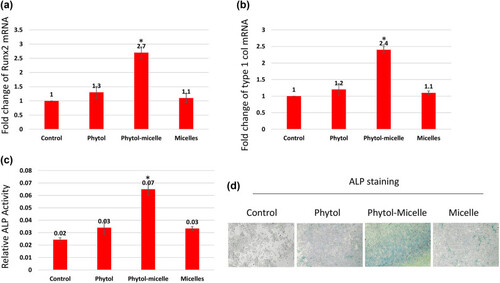
Molecular mechanisms underlying phytol-micelles effects on osteoblast differentiation. MG63 cells treated with 25 μg phytol-micelles in an osteogenic medium for 7 days showed increased mRNA expression of Runx2 (a) and type 1 collagen (b), along with elevated ALP activity (c) and ALP staining (d). * indicates a significant increase. |
|
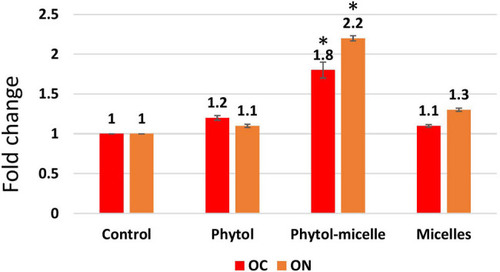
The enhanced secretion of OC and ON was observed. The data illustrate the enhanced levels of these bone matrix proteins, indicating improved bone formation and mineralization. * indicates a significant increase. |
|
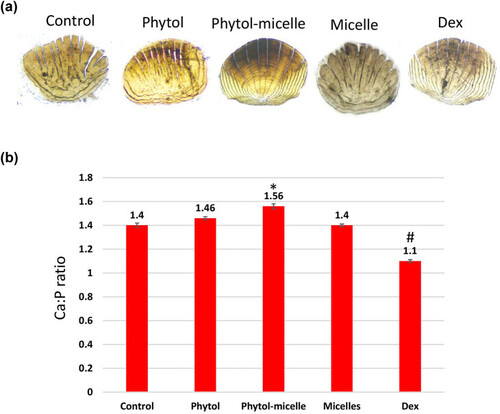
Phytol-micelles influence on calcium and phosphorus levels in zebrafish scales. (a) vonKossa staining of scales and (b) calcium and phosphorus content. * indicates a significant increase. # indicates a significant decrease. |
|
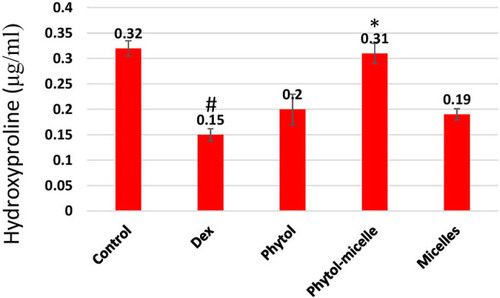
Dex treatment reduces HP levels in zebrafish scales, contrasting with phytol-micelles’ stimulatory effect, as depicted. * indicates a significant increase. # indicates a significant decrease. |
|
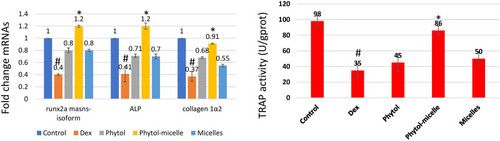
Dex treatment decreases ALP, runx2a mansn-soform, and collagen1a2 mRNAs but increases TRAP activity in zebrafish scales, contrasting with phytol-micelles’ stimulatory effect on ALP and inhibitory effect on TRAP activities, as depicted. * indicates a significant increase. # indicates a significant decrease. |
|
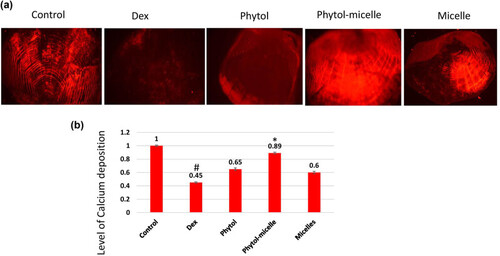
Dex treatment decreases alizarin red staining intensity (a), indicating reduced calcium mineralization (b) in zebrafish scales, contrasting with phytol-micelles’ stimulatory effect on alizarin red staining, suggesting enhanced calcium mineralization. * indicates a significant increase. # indicates a significant decrease. |
|
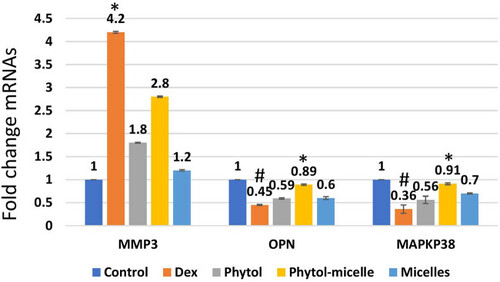
Dex treatment alters mRNA levels, reducing OPN and MAPKp38 while increasing MMP3 in zebrafish scales, indicating suppressive effects. Conversely, phytol-micelles significantly increase OPN and MAPKp38 mRNA levels while reducing MMP3, suggesting stimulatory effects. These molecular changes elucidate phytol-micelles’ potential mechanisms in bone metabolism and remodeling. * indicates a significant increase. # indicates a significant decrease. |