- Title
-
Adaptor protein Src-homology 2 domain containing E (SH2E) deficiency induces heart defect in zebrafish
- Authors
- Liang, Y.L., Hu, Y.X., Li, F.F., You, H.M., Chen, J., Liang, C., Guo, Z.F., Jing, Q.
- Source
- Full text @ Acta Pharmacol. Sin.
|
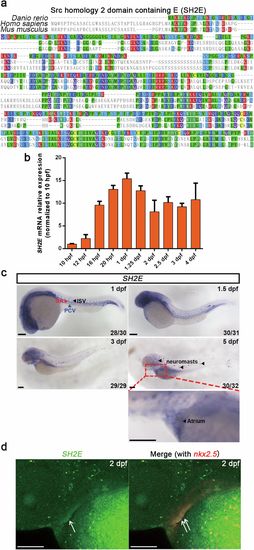
a Alignment of the zebrafish SH2E protein and its closest human and mouse homologs. b Quantification of SH2E mRNA expression levels at different developmental stages (15 embryos pooled per sample, n = 3). c Expression pattern of SH2E analyzed by WISH during 1 to 5 dpf, and the developmental time points are indicated in the panels. The ISVs are indicated by black arrowhead, and the DA and the PCV are indicated by red arrowhead and blue arrowhead, respectively. Neuromasts are also indicated by black arrowheads, and the region including atrium is magnified below. The number in the bottom right-hand corner indicates the representative embryos/total embryos. d Dc-FISH for SH2E and the myocardium marker nkx2.5 in 2 dpf embryos. For (c, d), scale bars = 100 μm. |
|
a Schematic structure of CRISPR targeting on zebrafish SH2E gene. Two target sites of CRISPR were designed in exon 1 to induce SH2E deficiency. The target sites of two restriction enzymes, Fnu4H I and Cfr10 I, are indicated with black triangles. +633 and +702 indicate the positions of PAM sequences. b The genotypes of embryos injected with Cas9 mRNA alone or with gRNA1/2 were confirmed by enzyme digestion using Fnu4H I and Cfr10 I, respectively. In each test, 10 embryos injected were randomly selected and pooled as one sample. c The mutated genomic sequences were confirmed by sequencing. d G59R fs and S82R fs are two types of mutants with frame shifts leading to early termination of protein translation. Δ12 and Δ6 are two types of mutants without frame shifts. The altered amino acid sequences are labeled in purple. |
|
a The arterio-venous differentiation and angiogenesis in SH2E+/G59R fs incross embryos with Tg(kdrl:egfp) background at 24 and 30 hpf. Scale bars = 100 μm. b The cardiogenesis of SH2E+/G59R fs incross with Tg(cmcl2:mcherry) background during 3-5 dpf. V, ventricle, A, atrium, scale bars = 100 μm. c The proportion of embryos with PCE in SH2E+/G59R fs incross (n = 3, ***P < 0.001 compared with the normal phenotype group). d Genotyping of SH2E+/G59R fs incross with PCE by Fnu4H I digestion. |
|
a The spatiotemporal expression of functionable SH2E mRNA in SH2E+/+, SH2E+/G59R fs and SH2EG59R fs/G59R fs derived from the same SH2E+/G59R fs incross. b The relative expression of functionable SH2E mRNA in SH2E+/G59R fs incross larvae with/without PCE at 5 dpf (15 embryos pooled per sample, n = 3). c The survival of SH2E+/G59R fs incross larvae within 12 dpf. d The morphology of 5 dpf SH2ES82R fs/S82R fs, SH2EΔ12/Δ12 and SH2EΔ6/Δ6 larvae. e The SH2E mRNA level in SH2E+/S82R fs incross larvae with PCE at 5 dpf (15 embryos pooled per sample, n = 3). For (b, e), *P < 0.05 and ***P < 0.001 compared with the normal phenotype group. |
|
a The SH2EG59R fs/G59R fs embryos with Tg(cmcl2:mcherrry) background developed dilated atrium compared to those with normal cardiac morphology (SH2E+/+ or SH2E+/G59R fs) from the same SH2E+/G59R fs incross at 5 dpf. V, ventricle, A, atrium. b The SH2EG59R fs/G59R fs embryos developed thickened ventricle compared to those with normal cardiac morphology (SH2E+/+ or SH2E+/G59R fs) derived from the same SH2E+/G59R fs incross at 4 dpf. V, ventricle, A, atrium. c An inducible SH2E overexpression system driven by Hsp70L was constructed. d The Tg(fli1:egfp) background SH2E+/G59R fs incross embryos injected with SH2E overexpression plasmids were heat shocked at 48 hpf. 8 h later (56 hpf), ubiquitously expressed red fluorescent could be observed in the trunk. TP, transposase. e Inducible overexpression of SH2E resulted in stable reduction of PCE by about 6% in SH2E+/G59R fs incross at 5 dpf. UIC, uninjected control; TP, transposase; n = 3; **P < 0.01 compared with uninjected control. For (a, b, d), scale bars = 100 μm. |
|
a Transcriptome sequencing volcano map of the SH2E+/+ siblings (from the same pair of parents as SH2E+/G59R fs) and the SH2EG59R fs/G59R fs mutants at 2 dpf. Fold change > 2 or <0.5, P < 0.05. Down-regulated genes are shown in blue dots, and upregulated genes are shown in red dots. b The DEGs in 2 dpf SH2EG59R fs/G59R fs embryos (15 embryos pooled per sample, n = 3). c Transcriptome sequencing volcano map of the SH2E+/+ siblings and the SH2EG59R fs/G59R fs mutants at 3 dpf. Fold change > 2 or <0.5, P < 0.05. Down-regulated genes are shown in blue dots, and upregulated genes are shown in red dots. d The DEGs in 3 dpf SH2EG59R fs/G59R fs embryos (15 embryos pooled per sample, n = 3). e GO annotation revealed that DEGs in 2 dpf SH2EG59R fs/G59R fs embryos enriched in developmental processes and molecular transmembrane transport processes. f The enrichment of DEGs in 3 dpf SH2EG59R fs/G59R fs embryos was similar to that in 2 dpf embryos. g Eight up-regulated and six down-regulated genes were overlapped between 2 and 3 dpf embryos, respectively. h The results of sequencing were further confirmed by rt-qPCR. Fifteen embryos pooled per sample, n = 3; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 compared with SH2E+/+ from the same SH2E+/G59R fs incross. |
|
Neither the transient overexpression of tcap (a) nor nphp4 (b) reduced the PCE ratio of SH2E+/G59R fs incross larvae at 5 dpf. (c, d)When treated with PD184352 (an MAPK/ERK signaling pathway inhibitor) from 10 hpf, much more SH2E+/G59R fs incross larvae developed PCE at 5 dpf, while with BAY11-7082 (an NF-κB signaling pathway inhibitor), significant fewer larvae developed PCE (e, f). g, h The number of 5 dpf SH2E+/G59R fs incross larvae with PCE increased after AKT inhibitor VIII administration. All experiments were performed 3 times independently, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 compared with the solvent control (the 0-concentration group). For (c, e, g), SH2E+/+ (from the same pair of parents as SH2E+/G59R fs) incross as the control. For (d, f, h), scale bars = 200 μm. |