- Title
-
Somatic RIT1 delins in arteriovenous malformations hyperactivate RAS-MAPK signaling amenable to MEK inhibition
- Authors
- Kapp, F.G., Bazgir, F., Mahammadzade, N., Mehrabipour, M., Vassella, E., Bernhard, S.M., Döring, Y., Holm, A., Karow, A., Seebauer, C., Platz Batista da Silva, N., Wohlgemuth, W.A., Oppenheimer, A., Kröning, P., Niemeyer, C.M., Schanze, D., Zenker, M., Eng, W., Ahmadian, M.R., Baumgartner, I., Rössler, J.
- Source
- Full text @ Angiogenesis
|
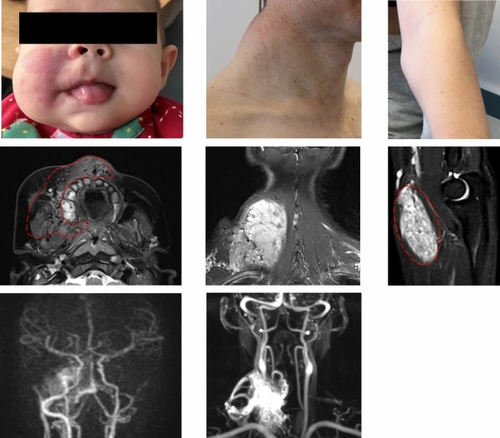
Three patients with somatic |
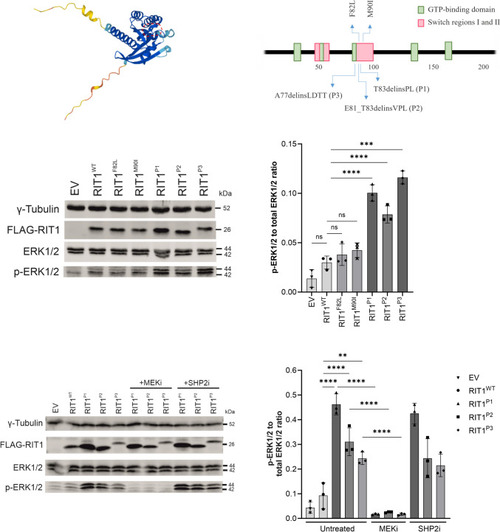
|
ERK phosphorylation after expression of |
|
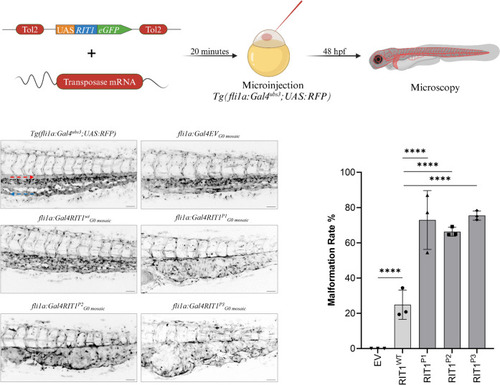
Endothelial-specific mosaic expression of |
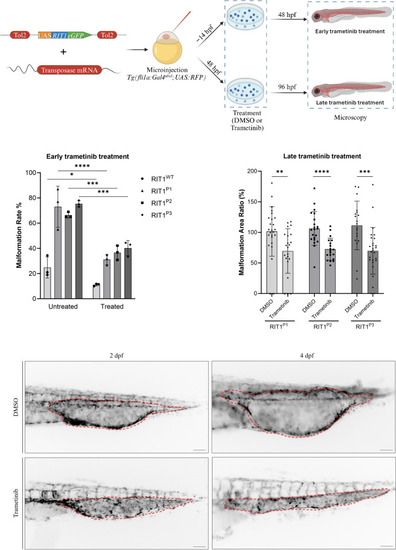
|
|
|
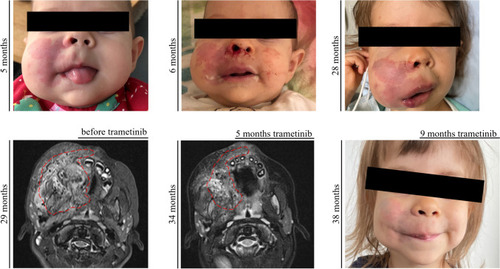
Response to targeted therapy in P1. |