- Title
-
Regulatory circuit rewiring and functional divergence of the duplicate admp genes in dorsoventral axial patterning
- Authors
- Chang, Y.C., Pai, C.Y., Chen, Y.C., Ting, H.C., Martinez, P., Telford, M.J., Yu, J.K., Su, Y.H.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Biol.
|
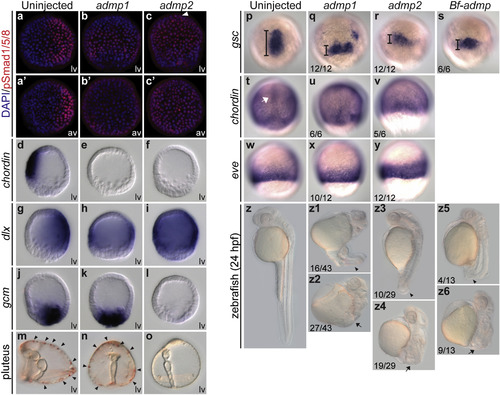
Functional analyses of Admp1 and Admp2 in the sea urchin and zebrafish embryos. Upon injection of mRNAs (300 ng/μl) encoding sea urchin Admp1 or Admp2, sea urchin mesenchyme blastula embryos were stained with an anti-pSmad antibody (a–c′) or hybridized with probes against the ventral marker chordin (d–f), the dorsal marker dlx (g–i), or the pigment cell precursor marker gcm (j–l). The white arrowhead in c indicates the animal pole. Pigment cells (black arrowheads) were restricted to the dorsal side of the normal pluteus larva (m), but were more broadly distributed in the admp1 mRNA-injected (n) and absent in the admp2 mRNA-injected embryos (o). The sea urchin embryos were viewed from the lateral side (lv) with the ventral side to the left or from the animal pole (av). Almost 100% of the injected embryos showed the phenotype displayed. (p-z6) Zebrafish embryos were injected with 200 pg of mRNAs encoding sea urchin Admp1, Admp2, or amphioxus Admp (Bf-Admp). The in situ hybridizations of the dorsal organizer markers gsc and chordin, and the ventral marker eve were performed at 70% epiboly, and the embryos were viewed from the dorsal (p–v) or ventral (w–y) sides. The length of the gsc expression domain is indicated by bars. The white arrow indicates the expression of chordin in the axial mesoderm. Zebrafish phenotypes were observed at 24 hpf (z-z6). The arrowheads and arrows indicate the reduced tail and absence of tail, respectively. The numbers in the bottom left-hand corners indicate the ratios of the displayed phenotypes. |
|
(a) The in situ hybridization of pks at the late gastrula stage labeled pigment cells in embryos over-expressing gfp (control) or admp1. (b) Quantification of pks-positive cells in injected embryos. The error bars are the standard deviation. (c) Sea urchin embryos injected with sea urchin admp2 mRNA lost both non-skeletogenic mesodermal cell lineages, including pigment cells (arrowheads) and blastocoelar cells (arrows, marked by col2a1 expression) at the gastrula stage. The in situ hybridizations of ese were performed at the mesenchyme blastula stage in control and admp2 mRNA-injected embryos. Embryos were observed from the lateral (lv) or vegetal side (vv), and the ventral side is to the left. (d) Two batches of zebrafish embryos were injected with 200 pg of mRNA encoding GFP and the phenotypes were observed at 24 hpf. The ratios of the displayed phenotypes are indicated at the bottom left corner. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 410, Chang, Y.C., Pai, C.Y., Chen, Y.C., Ting, H.C., Martinez, P., Telford, M.J., Yu, J.K., Su, Y.H., Regulatory circuit rewiring and functional divergence of the duplicate admp genes in dorsoventral axial patterning, 108-18, Copyright (2016) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.