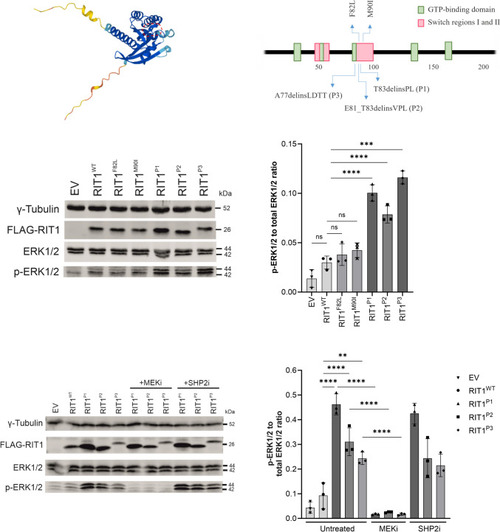
ERK phosphorylation after expression of RIT1 variants in vitro in HEK293T cells. a Protein structure of RIT1 predicted by AlphaFold, accessed through ensemble.org. The area labelled by the dashed red line indicates the switch 2 domain. b Schematic drawing of RIT1 functional domains of human RIT1 protein (green boxes = GTP-binding regions; red boxes = switch domain 1 and 2; blue arrows (upward) = two mutations typically found in Noonan syndrome; blue arrows (downward) = mutations identified in P1-P3. c Western blot after expression of RIT1 variants to assess RAS-MAPK pathway activation. Gamma tubulin served as loading control, FLAG-RIT1 confirms the expression of the construct, total ERK levels serve as a control to exclude the differential expression of ERK, and p-ERK measures the level of phosphorylate of ERK as a marker of RAS pathway activation. d Quantification of the ERK phosphorylation was measured in a total of three western blots for each variant (n = 3). One-way ANOVA. P value ***< 0.001; ****< 0.0001, ns = not significant. Data are presented as mean ± SD. EV = empty vector. e Western blot after expression of RIT1 variants and with or without treatment using a MEK inhibitor or SHP2 inhibitor. The same parameters were assessed as in panel d. f Quantification of the ERK phosphorylation was measured in a total of three western blots for each variant (n = 3). One-way ANOVA. P value **< 0.01; ****< 0.0001, ns = not significant. Data are presented as mean ± SD
|

